Adjusting the cyclic feed rate of the Bosch ve fuel injectors
To switch off the HPF for a longer period of time
If the engine, and therefore the fuel injection pump, is left unattended for any length of time, there should be no diesel left in the fuel injection pump.к. It becomes thick and viscous over time, the plungers and injection valves can seize and even become corroded. For this reason, before preservation you should add about 10% of a suitable rust preventative to the fuel tank and in the same proportion to the oil in the camshaft chamber of the HPF. The engine should then be run for approximately 15 minutes, during which time all the “normal diesel fuel” is flushed out of the HPF, which is at the same time effectively protected against fuel gelation and corrosion. New HPF that have already been effectively protected against corrosion in the factory are marked with the letter “p”.
Repair of Bosch HPF with RQVK regulators, installed on KAMAZ vehicles
This manual provides basic data for the repair and adjustment of high pressure fuel pumps 0 402 648 611, mounted on internal combustion engines of KAMAZ trucks. RQ and RQV regulators will be considered in comparison with RQVK mechanical regulators installed on KAMAZ engines.
In the video tutorial later we will show the complete repair of fuel injection pump on the example of a P-type fuel injection pump with RQV regulator. K.
Repair of HPF with RQVK regulators
1.1. General description of fuel injection pump assembly
Before you begin assembling the fuel injection pump it is necessary to wash and inspect its defects. Parts of fuel pump and nozzle bodies should be washed in drum-type washers, working on a closed cycle. The author has been using a Geyser washer with a 700mm drum diameter for the last 5 months.
When defecting parts of fuel injection pump and regulator the author recommends replacement of the following spare parts when plunger pairs are worn:
- 2 418 455 727. Plunger pair. 8 pcs.;
- 2 418 459 037. Discharge valve. 8 pcs.;
- 2 414 612 005. Valve spring. 8 pcs.;
- 2 410 422 013. Plunger swivel bushing (if there is ball wear, look with a magnifying glass 8x);
- 2 417 010 022. Hydraulic oil pump kit complete;
- 2 427 010 049. Fuel injection pump regulator repair kit;
- 2 421 015 057. Regulator gasket;
- 2,447,010,043. ANT valves repair kit.
Pay attention to the working surfaces of the camshaft, tappets, bearings and springs when reassembling. Clean the pump housing. Before rewashing it, remove any rings that may have remained after the plug sleeves were removed.
Figure 1.1 tools for plunger and tappet installation and tappet fixing are presented.
Plunger Fitting and Locking Tool Kit
The tappet retainer is positioned so that the part number stamped on the tappet housing is on top and the 0 mark on the pivot portion of the retainer is on the bottom. Install and remove the tappet stops on the cams fully depressed to prevent breakage of the stops.
Install the camshaft as shown in Figure 1.2.
Position of camshaft cams when installing and removing tappet stops
Install the camshaft as shown in Figure 1.3.
Installing the Camshaft in the HPF
Note that it is easier to remove and install the camshaft from the regulator side of the HPF shown in the photo. Many models use tapered bearings. Therefore, removal of the camshaft should be done through the front of the HPF after removing the front crankshaft bearing cap.
Dismantle and install the camshaft in the fuel injection pump case with the help of the press or with light strikes through the copper or aluminum casing.
It is recommended to carry out all percussion works with rubber hammers.
Metal plugs should be used only once.
Alignment of HPF on the bench
The assembled fuel injection pump is installed on the stand. Initially adjust feed angles of fuel injection pump sections according to the test plan.
Fig. 2.1 shows connection of test fluid supply to HPF on the test bench. The flow connection point is indicated on the test plan for each fuel injection valve. Connection point at the front of fuel injection pump. point 1, at the rear. point 2. Connection point of supply in our case is to point 3.2, to the return flow, respectively to point 3.1.
Connection points of fuel supply in the test liquid in HPF
Table 2.heights of plunger lifting on fuel injection pump of KAMAZ trucks of different models, at which overlapping of fuel supply occurs, are indicated.
When adjusting the angles, the plug is installed instead of the check valve and the pressure is maintained at 26 bar, the stroke of the rail and the lifting height of the plunger correspond to the data in Table 2.1. Then there is the beginning of feeding by sections of fuel injection valve in accordance with the test plan. in our case it is 1. 7. 5. 2. 4. 3. 8. 6 with step of 45 degrees.
To adjust the moment of fuel overlap adjustment use quality regulating washers. In practice there are washers of “left” producers, which thickness differs from the stamped on the washer by 0,05 mm or more.
The rail exit fixture can be made similarly to the one shown in Figure 2.2.
Fig. 2.3 shows the adjustments for rack stroke and plunger lift height. The values of all parameters must not exceed those specified in the test plan.
Installing Valve Stroke and Plunger Lift Height Measurement Devices
When setting the fuel shut-off torque, note that Bosch plunger pairs do not shut off the fuel supply completely in most cases. Drops may fall at intervals of 1 drop per second (or possibly more frequently).
Then according to the test plan set the beacon of fuel supply. This operation should be performed on all fuel injection pump assemblies. In our case, set the limb of the stand in 270 degrees from 1 section, which corresponds to the beginning of the 8th section feed and set the leading cargo coupling half-coupling, as shown in Figure 2.4.
Installation of the fuel start beacon
After completing the repair, install the fuel pump drive and set the beacon as shown in Figure 2.4, check the alignment of the marks on the housing of the HPF and the drive coupling.
Before reassembling the tapered surfaces of the camshaft and the coupling bracket, degrease and prime with Loxeal 82-21 or similar and torque 75 Nm.
In Figure 2.Figure 5 shows the assembly of the spring assembly of the mass clutch.
Spring Assembly of Cargo Clutch
It should be noted that unlike RQ and RQV regulators spring units there are no adjustments in this unit except for tension nuts (see below). ESI(tronic) specifies RQ and RQV thrust washers and bushes in section D (Parts), but these are not commercially available
The springs of weights and seats should not be deformed and have no breaks. Assembly of the spring unit must comply with section D (spare parts) of the ESI(tronic). The protrusion of the stud bolts of the assembled spring units must be 1 mm (6). Assemble the compression springs in accordance with the diagram in the ESI(tronic) manual. For the next adjustment procedure this dimension can be altered from 0 (flush nut on the stud) to 2.5 mm. The projection on both studs must be the same!
Basic adjustment of the stud projection 1 mm (0. 2.5 mm is permissible)
Adjusting the axial movement of the clutch
Then mount the coupling weights without rubber buffers to adjust their axial stroke, as shown in figure 2.7. Nut tightening torque 75 Nm. The coupling should rotate freely, but should not have any axial movement. Adjustment should be carried out using a round washer. Thickness of shims from 1.60 to 2.14 mm in 0.03 mm increments. It is recommended to reduce the thickness of washers until the clutch begins to clamp, then increase the thickness of washers until the clutch turns freely, then install the dampers and tighten with the prescribed torque of 65. 75 Nm.
Incorrect adjustment can cause camshaft liner breakage or irregular internal combustion engine operation!
Then adjust the vertical and horizontal dimensions of the lever group as shown in Figures 2.8 и 2.9.
Horizontal dimension 67,3 mm
Vertical Dimension 135.8 mm
Horizontal dimension 67.3 mm is axis centers, vertical dimension 135.8 mm is hole axis center. center of K-board (beveled part). These dimensions are valid for all RQVK regulators, mounted on fuel injection pump of P dimension.
Correct adjustment of the horizontal and vertical dimensions reduces the overloading of the regulator arm assembly.
Then mount the guide bush of the floating axle, replace the locking plates with new ones from the repair kit, torque of the bolts 6-8 Nm. Adjust the sliding bolt to the sliding distance from the regulator body using the 1 682 329 081 (10).
Adjusting the Sliding Bolt Spread
A drawing of the measuring fixture is shown in Figure 2.11.
Measuring device
Note that dimension L is 41,3 mm for fuel pumps for KAMAZ engines. Dimensions not shown are not important and are to be selected by the customer.
The linch pin and spring retainers should be replaced with a new one from the repair kit.
Install lever block (12). Note that the washers under the spring retainer are adjustment.
Preparing to Check Coupling Stroke
Install the indicator head with a preload of at least 15 mm as shown in figure 2.12. Use an indicator head with a stroke of at least 25 mm.
In the section REGUL. FOLLOWS. PULSE /SLAVE clutch positions at various speeds of the pump camshaft are shown. The position of the rack should be fixed at 9 mm. The strokes of the clutch at various speeds should be as shown in Table 2.2.
Precision vs Bosch Fuel Injectors
Adjustment is made by turning the nuts of the coupling weights. Allowed protrusion of the nut from 0 to 2,5 mm (6).
There is a high probability of installing the clutch weights from the “similar” fuel injection pump by previous overhaulers. It is therefore imperative that these measurements are monitored and adjusted to ensure that the limits are met. Parts of the clutch are not supplied as spares. Only this adjustment should be performed with the regulator cap removed.
Next install the full load limiter. Before installing the limiter, check the catalogue number and the number stamped on the housing. Refer to Table 2.Table 3 shows restrictor applicability at fuel injection pump of KamAZ vehicles.
Figure 2.13 Installation of the full load limiter is shown. It should be set in such a way that when the K-board hits the point indicated in the right side of the figure as the position at n = 900 and 1100 rpm, the stroke of the rack is 12 mm.
Installation of full load limiter
Then mount the cover of the adjuster. The rocker arm pin should be tapered notch up. Install a new gasket for the regulator cover. Then mount the driving levers axle and tighten their plugs and screws fixing the fuel injection pump cover with 6-8 Nm torque.
Before making any further adjustments, pour 200 to 300 grams of engine oil into the crankcase of the fuel injection pump.
To understand the adjustment process, I also recommend drawing the external speed characteristic of the regulator, as shown in Fig. 2.14. On this diagram it is required to show actual positions of the rack depending on camshaft speed. The adjustment points at the maximum load position of the control lever are shown in the diagram.
External HPF regulator speed characteristics
Install the fixture in the position shown at the left side of the chart.15. In the right part of the figure it is set to the position of the maximum fuel feed control lever of 119 degrees (permissible values from 115 to 123)
Control Lever Angle Gauge
Section VOLUME AT FULL SPEED. At this position of the control lever, set fuel pressure of 2 bar (use by-pass valve 1 417 413 047 given in the test plan) set camshaft rpm to 1100 rpm. At the same time the stroke of the rack should be 12 mm, and the volume of test fluid flowing through the bench nozzles. 174 cm3/1000 cycles. In this case the allowed difference of fuel supply to sections of fuel injection pump will be not more than 5 cm3/1000 cycles.
If stroke is below 12 mm, the reason should be determined. This is either the regulator has started acting and the rail has started ejecting, which can be checked by lowering the camshaft RPM. Either the K-board is not touching at its maximum load point and its angle needs to be changed.
Section MAX. DECREASING CYCLIC FUEL SUPPLY / REGULATOR. Set the number of 1150 revolutions per minute, the stroke of the rack should decrease to 11.0 mm, at the number of revolutions 1230. 4.0 mm, at the number of revolutions 1300. 0.5 mm.
Section idle stroke (lower part of the diagram). Next, set the control lever position to 71 degrees (allowable values from 67 to 75 degrees) for idle stroke adjustment. Stroke of the rack in idle stroke mode is 5.3 mm, cycle rate is 13 cm3/1000 cycles. In this case the allowable difference of fuel supply to sections of fuel injection pump will be no more than 6 cm3/1000 cycles. Further we reduce the rpm to 200, the stroke of the rack increases. At higher rpm the stroke of the rail decreases. This is the principle of operation of the regulator.
Adjust the RPM to 1150 RPM. In this section we check the stroke of the rack at various revolutions (Table 2.4). I recommend to check the fuel irregularity on these measurements as well, even though the test plan does not contain these recommendations.
Repair of Bosch fuel injection engines with RQVK regulators, installed on KAMAZ vehicles
This manual gives basic data for the repair and adjustment of high pressure fuel pumps 0 402 648 611, mounted on internal combustion engines of KAMAZ trucks. RQ and RQV regulators will be compared with RQVK mechanical regulators, installed on KAMAZ diesel engines.
In the video tutorial later you will see complete repair of fuel injection pump by the example of any Bosch type P injection pump with RQV regulator. K.
Repair of HPF with RQVK regulators
1.1. General description of fuel injection pump assembly
Before starting to assemble HPFD it is necessary to make washing and defectology. Parts of fuel pump and nozzle bodies should be washed in drum-type washers, working on a closed cycle. The author has been using for the last 5 months a 700 mm drum diameter Geyser washer.
The author recommends replacement of the following parts in case of wear of the plunger pairs during defect examination of the fuel injection pump and regulator parts:
- 2 418 455 727. Plunger pair. 8 pcs.;
- 2 418 459 037. Discharge valve. 8 units.;
- 2 414 612 005. Valve spring. 8 pcs.;
- 2 410 422 013. Plunger swivel bushing (if there is wear on the ball, look with a magnifying glass 8x);
- 2 417 010 022. Fuel injection pump kit, complete;
- 2 427 010 049. HPF regulator repair kit;
- 2 421 015 057. Adjuster gasket;
- 2 447 010 043. Oil Country Valve Repair Kit.
When reassembling, check camshaft, tappets, bearings and springs. HPF housing should be cleaned, before washing remove any rings left after the plunger sleeves have been disassembled.
Figure 1.1 tools for installing the plunger and tappet and securing the tappet are presented.
2 421 015 057. Control rod gasket; 1. Plunger insertion and locking tool set
Tappet retainer position is that the catalog number is on the top of the tappet body and the 0 mark on the pivot part of the retainer is on the bottom. Install and remove the tappet stops with the cams fully depressed to prevent breakage of the stops.
Install the camshaft as shown in Figure 1.2.
Position of camshaft cams when installing and removing tappet stops
Install the camshaft as shown in Figure 1.3.
Installing the camshaft of HPF
It should be noted that it is more convenient to dismantle and install the camshaft on the regulator side of the HPF shown in the photo. Many models use tapered bearings, so the camshaft should be disassembled through the front of the HPF after removing the front crankshaft bearing cap.
Disassembly and reassembly of the camshaft into the HPF housing should be carried out with a press or by lightly knocking it through the brass or aluminum drift.
All percussion work should be performed with a rubber mallet.
Use metal plugs once.
1 1 Adjustment of HPF on the bench
assembled fuel injection pump is installed on the stand. Initially adjust feed angles of HPF sections in accordance with the test plan.
Picture 2.1 shows connection of test fluid supply to HPF on the test bench. The point of feed connection is indicated in the test plan for each HPF. Connection point at the front of fuel injection pump. point 1, at the rear. point 2. Feed connection in our case is made to point 3.2, in the return flow to point 3.1.
Connection points of fuel supply to HPF
Table 2.heights of plunger lifting on fuel injection pump of KAMAZ trucks of various models at which the fuel supply is cut off are indicated.
At angles adjustment the plug is put instead of check valve and pressure 26 bar is supported, stroke and height of plug rise correspond to the data from Table 2.1. Then make the values of the beginning of the feed by sections of fuel injection valve according to the test plan. In our case it is 1. 7. 5. 2. 4. 3. 8. 6 in 45 degree steps.
To adjust the fuel shutoff torque rise use quality adjustment washers. In practice there are washers from “left” producers with the thickness differing from the stamped on the washer by 0,05 mm or more.
Adjustment for rack exit can be made similar to the one shown in figure 2.2.
Fig. 2.3 shown are the adjustments for the stroke and lifting height of the plunger. All parameters must not exceed the values stated in the test plan.
Installing fixtures to measure the stroke of the rail and the height of the plunger lift
When setting the fuel shutoff torque, note that Bosch plunger pairs do not shut off the fuel supply completely in most cases. Drops at intervals of 1 drop per second (and possibly more frequently) are acceptable.
Then according to test plan set the beacon of fuel supply. This should be done on all fuel injection pumps. In our case, we set the limb of the stand in 270 degrees from 1 section, which corresponds to the beginning of the 8 th section and install the driving coupling cargo coupling half, as shown in Figure 2.4.
Installing the Fuel Start Beacon
After completing the repair, install the fuel injection pump drive and set the beacon as shown in Figure 2.4. Check the alignment of the marks on the housing and the drive coupling.
Before assembly the tapered surfaces of the camshaft and the driven coupling half to degrease, treat with composition Loxeal 82-21 or similar and make tightening with the torque of 75 Nm.
Picture 2.5 shows the structure of the load clutch spring assembly.
Weights clutch spring assembly
Note that unlike the RQ and RQV spring clutch assembly, there are no adjustments in this assembly other than the tensioning nuts (see below). Section D (spare parts) of ESI(tronic) specifies regulating washers and bushings for RQ and RQV regulators, but they are not available on sale
The springs and seating should be free of deformations and cracks. The assembly of the spring unit must be in accordance with Section D (spare parts) of the ESI(tronic). The protrusion of the studs of the assembled spring units must be 1 mm (6). Assemble the spring units in accordance with the diagram shown in the ESI(tronic). For the next adjustment it is possible to vary this dimension from 0 (flush nut) to 2.5 mm. The protrusion on both studs must be the same!
Basic setting of the stud projection 1 mm (0. 2.5 mm is permissible)
Adjusting the axial movement of the clutch
Then mount the coupling weights without rubber buffers to adjust the axial movement, as shown in figure 2.7. Tighten the nut to a torque of 75 Nm. The coupling should rotate freely without any axial movement. Adjustment should be carried out using a round washer. Thickness of shim washers is 1.60 to 2.14 mm in 0.03 mm increments. It is recommended to reduce the thickness of the shims until the clutch is tightened, then increase the thickness of the shims until the clutch can turn freely, then install the dampers and tighten them to the prescribed torque of 65 to 75 Nm.
In case of improper adjustment, camshaft shank breakage or irregular operation of the internal combustion engine is possible!
Next adjust vertical and horizontal dimensions of the lever group as shown in Figure 2.8 и 2.9.
Horizontal dimension 67.3 mm
Vertical dimension135.8 mm
Horizontal dimension 67.3 mm. this is the center of the axes, the vertical dimension 135.8 mm. the center of the hole axis. the middle of the K-board (beveled part). These dimensions are valid for all RQVK regulators fitted to P.
Correct adjustment of the horizontal and vertical dimensions reduces the overloading of the regulator arm.
Then mount floating axle guide bush, replace fixing plates with new ones from repair kit, tightening torque of bolts 6-8 Nm. Using the 1 682 329 081 (10) fixture adjust the projection of the slide bolt from the regulator body.
Adjusting the projection of the slide bolt
Drawing of measuring fixture is shown in Fig. 2.11.
Measuring device
Note that for fuel pumps installed on KAMAZ engines the dimension L is 41,3 mm. Other dimensions are not important and must be selected by the customer.
Stop pin and spring retainers should be replaced with a new one from repair kit.
Installing the lever block (12). Note that the washers under the spring stopper are adjustment.
Preparing for checking the clutch stroke
Install the indicator head with a preload of at least 15 mm, as shown in figure 2.12. Indicator head to be used with a minimum stroke of 25 mm.
Under REGUL. FOLLOW-UP SIGNS. PUSH/CCP PATTERN positions at various pump camshaft speeds are indicated. The position of the rack should be fixed at 9 mm. Strokes of the clutch at different speeds should correspond to those shown in Table 2.2.
Adjustment is performed by turning the nuts of the clutch weights. nut can protrude from 0 to 2.5 mm (6).
There is a high probability of installing the clutch weights from the “similar” fuel injection engines by the previous repairers and there is also a possibility of slackening of springs. It is therefore essential that these measurements are monitored and adjusted to ensure that the specified limits are met. Weights clutch parts are not supplied as spare parts. Only this adjustment should be done with regulator cover removed.
Next, set the full load limiter. Before fitting the restrictor, check the part number and the number stamped on the housing. In Table 2.3 the limiters applicability on fuel injection pump of KamAZ cars is indicated.
Figure 2.13 indicates installing the full load limiter. Install it in such a way that when the K-board hits the point indicated in the right side of the figure as the position at n = 900 and 1100 rpm, the stroke of the rack is 12 mm.
Installing full load limiter
Next, install the regulator cover. At the same time the rocker arm should be tapered notch upward. Install a new regulator cover gasket. Then mount the driving levers axle and tighten their plugs and screws fixing the fuel injection pump cover with torque of 6. 8 Nm.
Pour 200-300 grams of engine oil into the crankcase before any further adjustments.
For better understanding of the regulation process, I also recommend to draw the external speed curve of the regulator, as shown in Figure 2.14. In this diagram it is necessary to draw actual positions of the rack depending on camshaft revolutions. The following diagram shows the adjustment points at the position of the regulator control lever at maximum load.
External speed characteristic of HPF regulator
Set the fixture in the position of the angle gauge as shown on the left side of Figure 2.15. In the right part of the figure it is set in position of control lever of maximum fuel supply 119 degrees (permissible values from 115 to 123)
Control lever angle device
Section VOLUME AT FULL OPERATION. At this position of the control lever with fuel pressure of 2 bar (using the by-pass valve 1 417 413 047 indicated in the test plan) set the camshaft speed to 1100 rpm. Herewith rack stroke should be 12 mm and test fluid volume, flowing through test nozzles should be 174 cm3/1000 cycles. Allowable difference in fuel supply by HPF sections will be not more than 5 cm3/1000 cycles.
If the stroke is less than 12 mm, determine the cause. This is either the regulator began to act and began to eject the rack, which can be checked by reducing the number of revolutions of the camshaft. Or it is K-board touches not at the point of maximum load and it is required to change its angle.
MAX section. DECREASING OF CYCLIC FUEL SUPPLY / AGGREGATE REGULATOR. We set the 1150 rpm, the stroke of the rack should decrease to 11.0 mm, at 1230 rpm. 4.0 mm, at 1300 rpm. 0.5 mm.
Idle stroke section (lower part of the diagram). Next, set the control lever position to 71 degrees (allowable values from 67 to 75 degrees) for adjustment in idle mode. The stroke for idle stroke is 5.3 mm, and the cycle rate is 13 ccms/1000 cycles. In this case the allowable difference in fuel supply by sections of fuel injection pump will be no more than 6 cm3/1000 cycles. Further on, the stroke of the slat should go down to 200 RPM, in this case the stroke increases. At higher RPM the stroke decreases. This is the principle of regulator work.
Section EQUATION. In this section we control the rail motion at different revolutions (table 2.4). I recommend to check the fuel irregularity on these measurements as well, despite the fact that the test plan does not contain these recommendations.
Buy Bosch HPVD KAMAZ EURO 3, on favorable price or order repair!
Repair Service
Easy and fast: parts and repairs in one place. Technical center, warehouse and diesel laboratory at your service.
Almost until the beginning of the new millennium, Kamsky Automobile Plant in the production of engines used domestic development of modifications of high pressure fuel pumps and other equipment. However, the increased requirements to emission standards has caused the need to modify the power units. In the process of transformation and improvement of the quality characteristics of the engine, the automobile manufacturer, in addition to products of the Yaroslavl plant, began to use fuel pumps Bosch
Proposals from German manufacturers were fully consistent with the goals and objectives of the modernization of engines, and therefore the choice of Bosch Euro 3 KAMAZ HPF was obvious.
Standard production of KAMAZ diesel power units provides for two types of fuel pumps with different fuel supply designs:
- The Bosch inline fuel system of P7100 type, which ensures continuous operation of the vehicle while supplying fuel to the fuel pressurized sections by a high-pressure fuel pump according to the strictly set parameters. Due to the cyclic nature of the process, which is determined by the operating mode of the power unit, the pump supplies high-pressure fuel in strictly dosed portions and sprays it into the combustion chambers. The speed regulator, which corrects the fuel quantity depending on the load and keeps the set rpm. The engine speed regulator, controlled by an electronic pedal module, is “responsible” for the functionality of the high-pressure fuel pumps.
- Accumulator fuel system, developed on the technologies of Common Rail, where the processes of pressure and fuel injection are separated, a certain level of pressure at injection is created and adjusted by the fuel pump and is practically unrelated to engine speed and cyclic fuel supply. This principle of operation ensures maximum optimization of the fuel injection process., and use of Bosch Euro-3 petrol injectors helped to improve the accuracy and responsiveness of the fuel regulation system and add the option of fuel temperature and engine thermal condition correction.
Modernization of KamAZ diesels with German fuel systems allowed to provide:
- increased injection pressure;
- regulated fuel supply process;
- pre-injection, if necessary, repeatedly, and then, late injection;
- Adjustment of the injection pressure in accordance with the operating conditions of the power unit and the vehicle;
- Precise dosing with the possibility of electronic adjustment depending on individual conditions;
- Reduction of engine noise and vibration.
The company Digital Diesel, cooperating with the German company for more than fifteen years, offers to buy Bosch fuel injection pump Bosch Euro-3, which can fully restore the functionality of the power unit of the truck without violating environmental standards, but using the advantages of the device
For German models the in-line design of the device is characteristic, which significantly increases the length of the product as an assembly, but at the expense of this the width of the pump is reduced. The camshaft, located below the superchargers and the cams are the main elements in organizing the sequence of the sections, their displacement relative to the common axis makes it possible to act on the plunger pairs, so they are triggered at specified intervals. over, nearly all models of this type, from German manufacturers, are made in such a way that the shaft drives both the fuel pump and the revolutions governor.
The cams act on the piston pairs via a pusher, which is spring-loaded in a free position against the cams. The special design of the articulation allows not only progressive motion, but also a partial rotation around the longitudinal axis, so that a defined advance angle is created in the groove-spiral, which, if necessary, can be changed through a number of adjustments-adjustments.
All necessary adjustments with thorough diagnostics of engine work allows the staff of skilled workers and special equipment, which the company Digital Diesel has at its disposal. Applying to the company’s Diesel Center makes it possible to;
- promptly identify possible malfunction;
- replace the necessary parts;
- Make unit or complete car repair,
use of original spare parts and units, supplied by well-known brands, i.e. to take a set of measures that will help to restore performance and extend the life of the car. Digital Diesel is a partner of the German concern and provides guarantees for the products sold and services rendered.
We are the only online auto parts store on the market, which offers everyone unique discounts for auto parts. up to 48%, including.ч. Bosch range.
This page provides part information for this product category. All information. prices, availability and delivery times are strictly true.
A little above you can find a parts search form for the Digital Diesel range. For 15 years our warehouses have about 20 000 of spare parts in stock, in the shortest possible time we can select and deliver any range of auto parts. If you do not have something or you need help. please contact us in chat or by phone number in the upper right corner. we are happy to help you for free.
If the page contains a large number of parts, please specify what you need in the chat or by phone. our hot line is free.
Sincerely yours, CEO of Digital Diesel – Sergey Cherniavsky
Repair of Bosch VP44 high pressure fuel pump number 059 130 106D
The pump number 059 130 106D was installed on: Volkswagen Passat B5.5 / Volkswagen Passat B5.5 (3B3) 2001. 2005 Volkswagen Passat Variant B5.5 / Volkswagen Passat Variant B5.5 (3B6) 2001. 2005 Volkswagen Passat B5 / Volkswagen Passat B5 (3B2) 1997. 2001 Volkswagen Passat Variant B5 (3B5) 1997. 2001 Audi A4 B5 / Audi A4 B5 (8D2) 1995. 2001 Audi A4 Avant B5 (8D5) 1996. 2002 Audi A6 C5 / Audi A6 (4B2) 1997. 2005 Audi A6 Avant / Audi A6 Avant (4B5) 1998. 2005 Audi A8 (D2) / Audi A8 (4D2) 1994. 2002 information is suitable for repair and other vehicles.
Hi, I’ve decided to write a report on repairing Bosch VP44, part number 059 130 106D, Audi A8 D2.5tdi V6, but this pump has been used everywhere, Audi A4, A6, VW, BMW, Opel, on trucks. So I guess the information can’t hurt. I have not had any experience with the fuel injection pump. So I’ve been asking a lot of questions from specialists on different forums. Thanks to everyone who helped with advice The report from the owner of an Opel Vectra played a big role. Mitrofan (thank you). The disassembly process is shown there. I want to tell you about my experience and my own “rake”, so that no one would jump on it unnecessarily.
So, you have nothing after pumping with a pear or anything from the injector tubes when you crank it with the starter. you have a problem with the manual: the most probable scenario. a damaged diaphragm (or rubber rings), the second option. The defect in the booster pump. You can see all this later on in the pictures. Who has everything in order. here you can see the fuel injection pump from all angles, including.ч. his most intimate parts
For starters, as long as the pump is on the car. We align the timing gear and the fuel oil pump in the “base” position, so that the hole for the stopper coincided with the hole on the pulley (shine a flashlight), to rotate the timing gear can either by crankshaft or camshaft (but not more than 75 Nm. smoothly, with pauses or transmission, hanging out the muzzle, turning the wheel. Then loosen the nut on the 27mm cog wheel, put a clear mark on the shaft and cog wheel. We may need it for reassembly. The tooth itself. the wheel sits hard on the “cone”. it even without the nut will not move a gram, it does not need to be pressed yet, for now we only need a mark with an awl:
The decision whether to compress it or not. we’ll do it later (not to do unnecessary work). Unscrew the pump from the car. nipples cover with something and rinse thoroughly with “kerher”, then we blast with carb cleaner in some places and blow with compressed air, so there will be less dirt while disassembling:
We unscrew the “brains” and the 2 el. of the valve (see Mitrofan for details), for this we need Torx 10,25,30 (T20 is also possible later). Before unscrewing, tap with a small hammer on the Torx if it doesn’t go. it’s better to keep tapping, because when you tear off the edges. We’ll have to drill and drive the “M” bit in.
When you pull the central flap (with a screwdriver as a lever), you must ensure that it comes out without tilting, if it tilts. Push it back in and try again with support from underneath.
Then bring the gear (which is still hard sitting on the cone) to the mark where the stopper is inserted (or, as for kolhoz, a drill 6mm), unscrew the T50 bolt, remove the washer under it and screw it to the stop, thereby blocking the movement of the shaft, stopper is removed:
The back will be in this position:
Next, to extract the distributor head according to Mitrofan unscrewing-unscrewing with screwdrivers, but I, in order not to spoil al. The body is just resting with a screwdriver and knocked down with a hammer:
Remove the distributor head and see the very defect that caused the loss of pressure. damage to the outer plastic part of the diaphragm:
If you see a picture like this (or just a crack). then there is no need to disassemble further. change the diaphragm and rubber rings and reassemble. The Bosch diaphragm repair kit 1 467 045 032. But there are some important nuances
Because I was inexperienced and did not notice at first. disassembled further:
Next to remove the bearing according to Mitrofan. pull with thick wire, I just put newspaper on the floor and hit with the body. By inertia the bearing and 2 washers came out:
Then you need to unscrew the plug, wrap the top with paper or rag and rip it out with pliers:
Using a punch or something handy, turn the cam washer and piston to the position where the cam. washer will slide up (in the photo turn it a little clockwise and it will rise):
After pulling out the clunker. washers. Pull out the piston. here is how it looks like from all sides (if it doesn’t come out well. It can be rocked with a prybar for 2 holes, which are in the photo at the top left, just do not stick deep into the hole):
Now press the gear wheel off the shaft (with the shaft “squeezed” by the Torx50 mentioned above, otherwise the shaft will shoot out like a bullet when removed. you can damage both the shaft and the housing). You will need a GOOD puller, the effort is HUGE, under the puller legs put good pieces of rags, so as not to leave “dents”.
After compressing loosen T50 and take out the shaft.
and the washer (what’s underneath). Remains in the housing the booster pump. Now use a T20 to unscrew the bolts (you need a long and thin T20, preferably):
It should be “shaken out” by hitting the body on a newspaper. then it will fall out “assembled”. If you try to push from behind with your fingers. It will most likely fall out “piece by piece”, that’s not good:
As they say it is undesirable to mix up the places of blades, otherwise they can be jammed on revolutions. pictures of it:
It is serviceable, the only thing is a small defect. pitting, but it is not criminal:
Sump pump was taken from spare donor pump, it fell out “in pieces”, flush it out. carb:
Then empty housing washed with “kerher” (without bringing close to the channels), then och. the carb through the ducts and compressed air dried. Clean:
Sump pump (donor) set in place:
We put a washer and put the shaft in (on the picture the washer is hanging on the shaft):
Align it on our mark-scratch with the shaft, then rotate until the stop hole is aligned and block T50:
Slightly stuff the tooth. wheel on the shaft, lightly push the nut on the 27mm. Put on the table the catalogs and damper tooth. of wheels, to put it comfortably for the further assembly. The picture is as follows, the shaft is locked in the “basic” position:
The piston rod was taken from a donor pump, I sanded the scratches a little with sandpaper P800, 1500, 2000. It is desirable to grind the bushing in the HPF housing with P2000 (but this is before washing).
As you can see on the left. piston ring interferes with assembly. just wrap plastic wrap around the piston, squeeze with your fingers and stick it in:
We put the piston so that the cam washer is “tucked” into it (yellow arrow). The second connection point of the cam. washers. black arrow:
And here is the cam washer itself, these are the 2 pins and need to be “inserted” into the holes:
Put the washers (which fell out with the bearing at the beginning of the report) lower. with the lettering down, the top one. with the lettering facing up:
The bearing is slowly hammered around the circle in place with a puncher (the end to wrap with painter’s tape or something softening)
Then put the rollers with their holders in place. Left 2pc. from the donor, right 2pc. from the main pump, slightly different in appearance, but kind of interchangeable in dimensions:
Winding up 2pc. Into the grooves (all the way, still partially peeking out in the photo):
Now we need to insert the distributor head. it’s donor, with the “correct” old all-metal diaphragm without plastic on the edge, which is hard to break (that’s why Bosch replaced it with a half-plastic one, to break it later and trade it in). Rinsed out. Carba, not yet dry:
Next, I put it in. and found that the hand turns the shaft only 1/4 turn and jams, I had to take it out and torture my brain. It turned out that here is also a catch from Bosch. in two pumps with the same number. Rollers of different lengths, these rollers (there are 2 pcs. in the hole):
Put “short” rollers. everything starts to turn easily. So pay attention to it when assembling. Cam washer and rollers to use from one pump or carefully compare.
Rasp. The head is gently put in place by successive tightening of the bolts:
And the 2 el. Return the valves to their lairs. All the rubber parts of the fuel pump assembly with grease, so that not to chew the lock T50 do not forget to remove and return the washer Shaft can be filed under the head and screwed slightly nut 27mm.
Put it under the hood, plug everything in, bolt everything to the car, hang the belt. Seric to the rescue: one and two. We’re only interested in the fuel belt.
When the belt is tensioned. Clamp the 27mm nut finally, I did 90Nm.
Started (albeit not immediately and with some fuss), it works:
Then when the cable arrives (from China). adjust parameters (cyclic feed and injection angle) on computer (VAG-Com) readings. Well, in the meantime drive, accelerates OK
P.S. A long time ago inexperience, unscrewed nipples from the donor pump. completely unnecessary, useless operation, but then I did not know and unscrewed everything I see. And now it is distributed. the head is “in business” and back the nipple can not tighten on the “pressed” copper washers. will leak.
Had to take 2 pieces of thick iron, put copper between them. the washer and on the vise anvil with light hammer blows to shape it straight. Then the washers sanded with an emery wheel on a stone (rough to P800), to remove “trace” from the nipples. After the smooth and beautiful washers in turn hang them on a piece of thick steel wire with a bent end, heat the fire until red and briefly several times immersed in cold water. If dipped for 1 time and held. It deforms strongly, and when a series of several as short as possible dips remains straight (or almost straight). After annealing:
Tightened the fittings with 65Nm, it is better to clamp the head in a vise, grasping the cast iron, for it was a little scary to pull, leaning on the 4 bolts screwed into the al. housing. With their task annealed washers. It works, it doesn’t leak.
Thanks again for your help I would like to add more details in the report (tightening torque, information about transistor, etc.).д.). I think we will gradually add and, if necessary, correct the report.
I wish you all less breakages of fuel injection pump assemblies. then successful, as far as possible free repair with your own hands without unnecessary operations
Actually those rollers which were in the way for assembly. it belongs to the plunger pair and change from one pair to another? It is not good to change them all in one pair. About the diaphragm. Somehow they were all iron. To disassemble with the tool, which indicated Bosch, I did not work Well and finally, here is the number of a set of rubber seals and copper washers: 1 467 045 046. Advance angle piston is not listed as it is different for each pump. diaphragm number: 1 467 045 032
I will also add on the adjustments that had to be made after assembly.
Injection Angle Adjustment. Link to report I probably wasn’t the first one to remove the pulley on my HPD, because it was running on the very edge of the reg. bolts, and now when I took off and put on during the repair, apparently a little more shifted (in spite of the scratch mark) and I was able to start it only when I shifted the fuel injection belt by a tooth, i.e.е. Marked the marker on the belt and on the pulley with a marker and after flipping the marker became as in the picture in red:
Then I corrected the final position and angle with 3 adjustments. with the bolts. In the future, it would be better to rearrange the pulley of the fuel oil pump so that it is set as by-will, hitting in the middle of the bolts and not rearrange the belt by a tooth Before the adjustment the angle came out 8.4BTDC, look here:
To change the value of the angle from 8.4 BTDC to 2.0 ATDC. had to shift on the inside near the bolts to
3mm and a little counterclockwise. Starts about the same as it did, with minimal delay, but not immediately.
When catching small values (let’s say from 2.4 we need to make 2.0). Put a scratch mark on the outside radius and shift the pulley by a very small amount:
BEFORE the angle was adjusted I had such problems that sometimes it was lagging and wouldn’t pick up speed (instantaneous fuel consumption is low and stays the same at 10-12L), then I would rev up to 4k., Switching. and rushes with a good pickup (and flow of 45L) “Error 00550: start of injection. adjustment range”. AFTER adjusting the angle. these problems are gone
Specially bought a handy T10 knob for the sensor. To unscrew the cap. Т25:
Unscrewed the 8 “brain” bolts and there it is, the sensor:
And plunged the wrench into a diesel swim I unscrewed, moved the gauge to the “driver’s” side (=decreasing the cyclic value), fortunately, the diesel “magnifies” the image and we can see how much has shifted. Before adjustment it was 6mpg on hot. Going in:
And in the 1st group look at the cycle rate in mg. Ended up putting about 3.8mpg on hot (85gr.).
Everything, traction is very good, starts, drives.
If you can not find information on your car. look it up for cars built on your platform. than likely the repair and maintenance info will fit your auto.
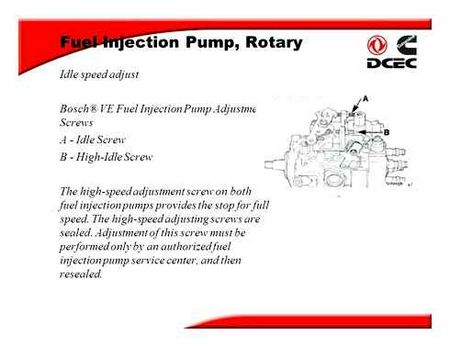
How to increase fuel flow to the fuel pump
Wandering around the Internet I came across an interesting article on our HPF from galloper forum and I couldn’t resist posting it. This article covers almost all of the adjusting bolts and nuts for our HPF. What does it do and how does it affect. In general I lay out (link to article:www.galloper.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=17t=2175) HPF is a VERY RESPONSIBLE assembly and it is VERY NOT RECOMMENDED to touch it without a special need. THE TVS NEED TO BE ADJUSTED ON THE BENCH. All adjustments to the HPF are interrelated. And it’s outrageous. HPF controls not only the fuel supply, but also the advance angle of injection. And in all modes and at all temperatures. That’s why if you adjust one thing, you can break everything else. Sometimes you are happy with the work of the fuel injection pump and you just have to fix something. If you approach it wisely and cautiously, you can do something yourself. And it’s not that small. It happens that you can’t even find a specialist in the countryside. And you don’t want to go many kilometers away. And it’s okay if I start turning the screws myself. the main thing is to remember how many rpm and which side of the screw you are turning. So you can put it all back. Use a good screwdriver to turn the screws so they don’t come off. The position of the screw should be memorized, or better yet, written down to fractions of a turn. We only turn what we know what it is and why we turn it. If you are not satisfied with the adjustment, put everything back. In this case, the risk of misalignment is minimal. The main risk is that we confuse how many revs we were turning. You have to be careful. Spin it, don’t be lazy to write it down. And save the paper. Maybe problems will start in the winter because of the knocked down adjustments (or in the summer). Gather and collect information from all over Internet. Created this thread to hear your opinions, additions and Комментарии и мнения владельцев. I think over time this post should be a good guide, if you help. We get into the fuel system quite rarely. Forgotten. Wouldn’t hurt to have a manual. Correct me if I wrote something wrong.
Beginning to do something with fuel injection pump should be to flush it. Here is a link to flushing the injection pump.www.pajero4x4.ru/bbs/phpBB2/viewtopic.php?t=14403forum.racing.kz/index.phpgopid=432483#entry432483If the tank and generally the entire fuel system is clean enough, no flushing can be done, but periodically adding injector cleaner directly to the tank. They say it’s no worse if used periodically. If there is a lot of dirt in the tank and pipes. clog the injectors to hell. And there’s no filter to help.Before you get upset about the poor performance of the fuel injection valve you should first take a look at the EGR. Valve diverts some of the exhaust gases to the intake. About that, whether you need it or not to write enough. But you should try to cut it off, sometimes engine work is fully recovered and you do not need to touch the fuel injection system. And then everyone decides for himself whether to drive with it or not. I’ve had it jammed, and then I’ve removed it altogether.In the same way, with the worn engine try to disconnect the crankcase ventilation tube from the intake. Seal the hole in the intake valve. Sometimes after that the engine is unrecognizable.Recommended next step is to do the following: Unscrew bolt 14. Do not lose 2 copper rings. Although it is better to replace them with new ones. The bolt is on the fuel drain. There is a tiny hole in the side of it. To keep debris out of it, there is a strainer in the bolt. Use a brush to wash debris out of the mesh in kerosene.Idle stroke adjustment screw 1. You can safely turn it without remembering how many revolutions. The risk to adjust something is minimal, but it is possible that you can’t set the necessary rpm because of the wrong settings. (In this case take HPF to the test bench for adjustment). Adjusting on a hot engine. RPM. 750-800 rpm (the first division on the tachometer. 0, the second. 500, the third. 750, the fourth. 1000). The air conditioner and other stuff should be turned off. In this case, the vacuum regulator 9 should not press.On some HPF the screw 1 is not installed where on the picture, but on the back of the HPF. But it presses on the same lever and adjustments are the same.Regulator of high idling speed 13 (regulator of quick idling). When the air conditioner, automatic transmission torque converter, etc. are on.д., use screws 2 and 3 to set the idle speed to 1100 rpm. If the gearbox is manual, up to 900 rpm is enough. Do it on a hot engine. The adjustment is very simple and you don’t need to remember how it was. According to the rules, with clutch 2 bring the rod almost close to the lever when the engine is stopped (about 1 mm clearance), and with screw 3 adjust the speed. Diaphragm in the regulator 13 is sometimes torn. In this case, you can drive fine for a while if you increase idling speed with the already known screw 1. I drove without the idle speed adjuster and with a new fuel injection valve it was never there at all.Use screw 4 to set the rpm on a cold engine to 1200-1500 rpm. This should be done when it is very cold, at.20C or lower after a night of standing idle. But when you turn the screw 4, be sure to remember how many revs. If after our adjustment the engine starts worse in the cold, quickly turn everything back. Wait for.20C hard. But already at 5C the regulator 12 slides in so much that it begins to press the lever 10. That’s why we do it that way. At 5C we turn the screw 4 until it makes contact. Be sure to record how much you have twisted, because despite the apparent simplicity of the adjustment is quite serious By the rules screw 11 adjusts the timing of injection in a cold engine, and the screw 4 revolutions. It’s not a good idea to do it yourself. I don’t think it’ll work. Especially if you turn the screw 11, you will lose the injection torque on a hot engine.Screw 6 to adjust booster compensator 7. Booster compensator increases the fuel dosage when the turbine comes into operation. To be more precise, it limits the fuel supply when the boost is insufficient. Hardly needs adjusting. The booster compensator itself 7 for the rupture of the diaphragm is checked simply. Take off the hose, put on another one, clean, suck air with your mouth and plug the hole with your tongue. If the tongue stays stuck for a long time, there is nothing wrong. If the diaphragm is torn and you don’t want to change it (by the rules entire fuel injection system should be changed)! I don’t know if it’s true), you can drive pretty well without it. It is only necessary to increase fuel supply at maximum RPM with the lever 8 (about this below). There will be a cloud of smoke when you suddenly press the accelerator pedal. and then everything is normal (fuel will go before the turbine picks up speed). But you won’t get full power anyway as the screw 8 influences the other modes of the engine and you shouldn’t turn it too much.Screw 9. maximum rpm adjustment screw. It hardly needs adjusting. Check if the lever 10 rests on the screw 9 when the pedal is completely depressed. It is not a good idea to turn it. In fact, if you twist it, you just do not press the gas all the way as it was before. If the lever 10 does not reach the screw 9, adjust the cable. It is already simple and I will not describe it. If by the rules, then with the accelerator pedal fully depressed the idle RPM should go up to 4200. It is possible to adjust it in this way.Screw 8 is the maximum fuel supply screw. Screw is EXTREMELY responsible. Turning it may screw up the whole operation of HPF. In addition, you need to turn it a fraction of a turn. It is also difficult to reach. By unscrewing the screw we move the plunger drain ring to the right, thus reducing the fuel supply. E.g. when the turbine does not develop pressure and you drive on, you can unscrew the screw a bit. Black smoke will disappear at high load, fuel consumption will decrease, but the engine will still be pulling just as badly. At a sharp pressure on the gas pedal at idle you should see a light cloud of black smoke from the exhaust pipe and after that the exhaust pipe is absolutely clear. This is optimum.If the antifreeze was dirty, the regulator may be clogged with dirt 12. In this case, when the engine is warmed up, the rpm will remain high for a very long time. Take off tubes from it (antifreeze will flow out)!) and blow it out with air.
Adjustment of Injection AngleAn initial injection torque angle is adjusted by loosening the screws on the fuel injection pump and turning it. For this injection valve the injection timing is adjusted according to the instructions with the indicator. The adjustment is standard and is described in the instructions extensively. Since the engine is not new, the injection angle is done a little earlier.And to put the pump back in place after cranking, first use a small chisel to put a little paint on fuel pump and fixing bracket, drop some white paint and wipe it off. This will always restore everything as it was.There is another tricky screw 11. This is on the device that adjusts the advance angle of injection on a cold engine. Injection angle also depends on the position of the screw 11. Turning the screw back gives an earlier injection. The device is operated by means of the cylinder 12 from which the piston rod moves out when heated with antifreeze. At.At 20°C and below the injection angle will be as early as possible. When the engine heats up from.20C to 50C the injection angle is getting later and later. The maximal late angle is reached at 50°C and does not change further. At the same time this device increases engine RPM at low temperatures. The screw 11 can also be used to adjust the initial angle of the injection torque. But by adjusting the injection angle, we reduce it on a cold engine. That is why you can use it only to try to change the injection angle. It’s convenient because you can do it without stopping the engine. Then everything is restored and the injection angle is adjusted by the position of the fuel injection pump.There is another method of adjusting the injection angle. This is not the method for the HPF. If you want to screw around, you can do it this way: Adjust the advance angle of injection with the help of “momentoscope”. The name of the device is serious, but the device itself is just a capillary. Remove the tube from the first nozzle. You put a piece of transparent hose about 10 cm long on the tube. At the other end of the hose put the capillary of the alcohol thermometer. From the mercury one is too thin. Another capillary is also possible. The rod from a ballpoint pen is thick. We fix the capillary vertically. We open the fuel supply at full throttle. We turn on ignition and twist the engine by hand by the crankshaft pulley bolt until the tube fills with diesel. Then bring the crankshaft to the beginning of fuel injection into the first cylinder. squeeze the thick tube so that a drop comes out of the capillary. Tapping on the key, turn the crankshaft in small increments until the capillary tube is filled with diesel fuel. This is the injection moment (to be very precise, the moment of injection will be a little later, when the pressure increases). There is only one BUT. What should be the injection valve timing according to the torque meter. nowhere specified. If you had to do this operation away from civilization, when there is no capillary, you can determine the time of injection just by the droplet that appears at the exit of the unscrewed pipe.There is a very good way to adjust, or rather to find the right injection angle. Choose a flat, quiet stretch of road. We accelerate to 60 km/h, for example. Put it in fifth gear. Near a tree, a pole, etc. п. We press the gas all the way down and measure the acceleration time, e.g. up to 120 km/h using a stopwatch. Go back to the same place. Change the injection angle and repeat the whole procedure. When we have the shortest acceleration time, that is when we have the optimum injection timing.The cycle fuel supply by the pump has always been constant, so the minimum acceleration time will correspond to the maximum efficiency of the engine. The angle will be optimized for our diesel, our worn out engine, our worn out and slightly out of adjustment fuel injection pump, our worn out turbocharger, our stretched belt, etc.д. Sometimes, if the engine is worn out, it starts to run hard after this adjustment. Well, then we do the advance a little bit later. If you’re interested in going really fast, you just determine the top speed. But it will be not quite right, because at low revs the angle can get far from the optimal.The solenoid valve is triggered when the voltage is applied and supplies a vacuum to the diaphragm 13. The electromagnetic valve is supplied with voltage not only from air conditioner but often from auxiliary device itself.Headlights, Loud music, etc.д. There should be voltage from automatic transmission as well. How this is implemented, I do not know. I have a manual transmission. I can only say that it is not possible to energise the diaphragm directly. There should be some sort of decoupling, either with relay or with diodes (otherwise you would get, for example, that you switched on air conditioner, it gave voltage to valve and then to auxiliary voltage).headlights).What to do if the diesel does not develop revs? Or, what is the same, does not pull at high revs. Or does not develop the maximum speed. The turbine and the compression is normal.In general, this problem I was not the only one. And no one has been able to solve it properly.And so. It’s been almost 3.5 years since I bought the Galloper. Top speed was 110 kilometers per hour. That’s the limit. RPMs are 3100-3200. I couldn’t even get it above 3500 at idle. BUT! At lower rpm everything was fine. And since I didn’t want to drive fast, I didn’t look for a reason.And now I flushed the fuel pump. Soon there was horrible air leakage through the fuel filter (nothing to do with the flushing). The filter was replaced with a kit from a Ford Mondeo 1.8TD. It’s also leaking. Bought a repair kit for it. I did it all. There’s no suction anywhere. Max idle RPMs are now down to 2500. You accelerate fast, and then you stop.After surfing the internet, I found a discussion on some forum. I didn’t take my own pictures, but I stole two pictures from there. I don’t think they will be offended as it says they want to put it out for Gallopers as well.And so. The reason was a little, little, little. There is a bolt on the inlet to the fuel injector. Washing all around from dirt. Unscrew it:
Don’t lose the 3 copper rings. At the same time we unscrew the clamp, which fixes the fuel pipe to the fuel pump. To get this tube out of the way. We take the copper rings home, heat them over a gas until they are red, and then immediately throw them in cold water. They will become soft. Or buy new ones. It is desirable to carry out a similar procedure with the new ones.From the hole, we remove the spring.In the depth of the hole (about 5 cm from the surface) there is a small mesh. It can be removed either with a stick or with absorbent cotton wrapped around it. Or, better yet, take a stranded wire, strip the strands by 7 mm. Unscrew it. Insert the wire and remove it together with the mesh:
We rinse the mesh, blow it out. It’s not cleaning. So after that we take it to the gas station. Let’s heat them up a bit. And flush it again, blow it out. It’s all clear.Reassemble everything in its place. The whole procedure was done under my window in the courtyard of my apartment. Took about 20 minutes. Went. The car is unrecognizable. The beast! Apart from that, the knocking noise at 3000 rpm is gone.Why is this grid so important?? It’s on the inlet to the fuel pump. When it becomes clogged, fuel injection pump starts sucking air through its seals. At low rpm it doesn’t suck. At high rpm the vacuum is higher and there is no leakage.There is a centrifugal speed regulator in the fuel injection pump. It’s under the top cover. When cranking the starter, it holds the fuel supply at maximum. When running at idle speed maintains rpm. If the engine is cold and rpm is low, the fuel feed automatically increases. If we turn the air conditioner on, rpm drops too. Regulator increases fuel flow again.Well, it looks like this. Switch on air conditioner. RPMs drop (you can barely see it on the tachometer) and the engine continues to run as if nothing happened.And the vacuum regulator additionally increases the RPM when the air conditioner is turned on. The air conditioner starts to cool a little harder at idle that’s about it.
Adjusting the HPF on the engine
The HPF is synchronized with the engine by means of the setting marks for the start of injection (closing of the channel). These marks are on the engine and on the HPF.
Usually the engine compression stroke is used as the basis (reference point for injection timing adjustments, although other options can be used for a specific engine model). In this respect it is important that the manufacturer’s instructions are observed. In most cases, the setting mark for closing the channel is on the engine flywheel, V-belt pulley, or vibration damper. There are several options for adjusting the HPF and setting the correct injection start (channel closure) value.
- The HPF is delivered from the factory with its camshaft locked at the set position. After mounting the HPF on the engine and bolting it down, with the crankshaft in the proper position, the HPF camshaft is released. This well-proven method is inexpensive and becoming more and more popular.
- The fuel pump is equipped with a channel closure indicator on the end of the regulator, which must be aligned with the setting marks when the fuel pump is installed on the engine.
- The timing advance device (clutch) has a closing point mark on the orifice, which should be aligned with the mark on the fuel injection pump housing. This method is not as accurate as the two previously described.
- After the HPF is installed on the engine, the high pressure overflow method is used on one of the pump outlets to determine the closing point (torque) of the channel (t.е. when the plunger overlaps the fuel outlet). This “wet” method is also actively replaced by method 1 and 2 described earlier.
Air bubbles in the fuel may impair or even make it impossible to operate the HPF. For this reason, devices that are installed for the first time or that are temporarily disconnected must be vented.
If the fuel priming pump is equipped with a manual pump, it is used to fill the line, fuel filter and fuel injection pump with fuel. The venting screws (1) on the filter cover and on the HPF should remain open until the exiting fuel is bubble free. Bleeding must be performed whenever the fuel filter is changed or work is performed on the system.
In real applications, the injection system is vented automatically through the by-pass valve (2) on the fuel filter (continuous venting). A restrictor may be used instead of a valve if the pump does not have a by-pass valve.
It is best to connect the fuel pump and regulator to the engine lubrication system, t.к. This form of lubrication leaves the fuel injection pump maintenance free. Filtered engine oil is fed to the HPF and regulator through the discharge line and inlet port through the roller tappet hole or by means of a special oil supply valve. In the case of a base or frame fuel injection pump, the lubricating oil return to the engine is via the return line (b).
in the case of a flanged mounting, lubricating oil return may be through the camshaft bearing (a) or through special passages. Before turning on the HPF and regulator for the first time, they must be filled with the same oil as the engine. in the case of a fuel injection pump without a direct connection to the engine oil system, oil is injected through the cap after removing the cap to remove air or filter. pump oil level is checked by removing the oil level screw on the regulator at the intervals specified by the engine manufacturer for changing oil in the pump. Excess oil (increased amount due to oil leakage from the lubrication system) must be drained and if there is not enough oil, top up with fresh oil. When the HPV is removed or the engine is overhauled, the lubricating oil needs to be changed. HPF and regulators with separate oil supply have their own dipstick to check oil level.
Bosch and Lucas injection advance angle setting
A dial indicator fixture is required for use with the oil level gauge. A drawing of the dial indicator housing is shown in Figure B6. 16. The holes in the fuel injection head for installation on the indicator in different years were made with different threads (M8x1 and M10x1). Shorter housings (option 1 and 3) are designed for work with HPF in cramped spaces and may be used only with removed high-pressure tubes. Longer housings are used when there is enough room and the high-pressure hoses can be left in place. The M5 threaded hole in the adapter is for the setscrew.
Note: the M5 stopper should be tightened easily by hand so that it does not catch on moving the indicator foot.
The original tip in the dial indicator is replaced by an extension tube Option 1 is used with short adapters, option 2 with long adapters.
Figure 16 shows the adapter of the simplest form, which in everyday use is not very convenient. advanced adaptor options are shown in Figure 8. 18 и 19.
order of performing the adjustment:
set the crankshaft in the TDC position, aligning the marks on the flywheel and on the fuel pump pulley; thoroughly wash the fuel pump in the area of the plunger head of dirt; unscrew the plug bolt on the end of the fuel pump plunger head (located in the center between the high pressure tube fittings). Check that the copper sealing ring is removed together with the plug; instead of the plug, screw in the adapter, insert the hour indicator with an extension leg into the adapter and lightly fix it with an M5 stopper, creating a preload of 3 mm on the indicator. slowly turn the crankshaft counterclockwise, watching the indicator hand. When the indicator hand stops moving, stop turning the crankshaft. In this position reset to zero on the large scale of the indicator, slowly turn the crankshaft clockwise until the mark on the flywheel aligns with the reel or a positioning pin hits the hole in the flywheel. In this position the indicator should show the value given in tab. 1.
Table 1 Plunger Stroke to TDC for Various Engine Types
if the indicator shows otherwise, without touching the crankshaft, loosen three bolts 3 on the fuel injection pump pulley and use wrench 2 to turn the fuel injection pump shaft until the indicator shows the set size. Tighten bolts 3 to 25 Nm; for X17DTL motor, remove flywheel pin; turn crankshaft counterclockwise until indicator hand stops moving and check to see if indicator is reading zero; turn the crankshaft around “to go” until the mark on the flywheel coincides with the reel or the locking pin hits the hole in the flywheel; check the hour indicator, which should match the set Some pumps have non-compound pulleys on the drive shaft. In these cases, adjustment of the UNPT is carried out by turning the housing of the fuel injection pump. To do this you need to detach the union nut high pressure tubes from the nozzles and close the nozzle nozzle connections with protective caps; loosen the union nut high pressure tubes on connectors fuel injection pump loosen the two most uncomfortable bolts on the mounting flange and the bolt on the bracket that supports the fuel injection pump from below near the plunger head; after loosening the third bolt on the mounting flange of the fuel injection pump by turning the pump to achieve the desired indicator reading and tighten the bolt; tighten the remaining bolts
Installation of UNOPT for engines with LUCAS HPF
Will need a test rod for operation. as well as a depth gauge (caliper) or a clock-type indicator on a stand, or a special hinged fixture with an indicator
The procedure for doing the work:
set the crankshaft at 90 degrees to the TDC of the first cylinder; thoroughly clean the top of the HPF; use a dipstick to unscrew the plug “A” from the boss on the HPF cap.
insert the control rod into the opened hole;
measure with depth gauge the distance from boss surface to upper end of control rod and write down the value.
If the readings differ from the set:
turn crankshaft “around” by 1 and 3 / 4 turns; insert control rod and measure the amount of protrusion; turn crankshaft to TDC position, aligning the mark on the flywheel with a turnbuckle or until a positioning pin hits the flywheel hole; measure difference between readings of measuring instrument, which must match those on the plastic plate; remove the control rod; install all removed parts.
Simplified scheme electronic control
a single-plunger VE fuel pump from Bosch for the diesel engine is shown in Fig. 4.
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of electronic control system of single-plunger HPF:
1. injection start sensor; 2. TDC and crankshaft speed sensor; 3. air flow meter; 4. coolant temperature sensor; 5. fuel pedal position sensor; 6. control unit; 7. gas pedal actuator for starting and warming up the engine; 8. Exhaust gas recirculation valve control servo unit; 9. Injection advance angle control servo unit; 10. Dispense clutch servo unit; 11. Dispenser stroke sensor; 12. Fuel temperature sensor; 13. HPF
The main regulating element of the system is the electromagnetic actuator 10 which moves the dosing clutch of the fuel injection pump.
Fuel supply processes are controlled by the control unit 6. Control unit receives information from different sensors: the beginning of injection 1, installed in one of the fuel injection nozzles, top dead center and crankshaft speed 2; air flowmeter 3; coolant temperature 4; fuel pedal position 5, etc. In accordance with the control characteristics set in the memory unit and the information received from the sensors, the control unit generates output signals to the actuators controlling the cyclic feed and the advance angle of fuel injection. Thus, the cyclic fuel feed rate is adjusted from idling to full load mode, as well as during cold start.
Potentiometer of the actuator sends a feedback signal to the electronic control unit, determining the exact position of the metering clutch. The advance angle of fuel injection is regulated in the same way.
The electronic control unit generates the signals ensuring flow of regulating characteristics, idling speed stabilization, exhaust gas recirculation, the degree of which is determined by signals from the mass air consumption sensor. The control unit compares the real sensor signals with the values in the programmed characteristic fields, resulting in an output signal to the servomechanism of the actuators, which provides the desired position of the metering clutch with high regulation accuracy.
The system is integrated with the program of self-diagnostics and working out of emergency modes, which allows providing movement of the car in case of the majority of failures, except for the microprocessor failure.
In most cases for single plunger pumps of distributive type, electromagnet 6 (figure 5) with a rotating core, the end of which is connected through the eccentric to the metering coupling 5, is used as an actuator which regulates the cyclic feed. When current flows in the coil of electromagnet, the core rotates by an angle from 0 to 60°, respectively moving dosing clutch 5, which changes cyclic feed.
Figure 5. Expanded diagram of single plunger pump with electronic control
1. HPV, 2. automatic advance-injection control solenoid valve, 3. nozzle, 4. automatic advance-injection control cylinder, 5. batcher, 6. electromagnetic device of fuel supply change, 7. electronic control unit, 8. temperature, boost pressure and fuel supply position sensors, 9. control pedal, 10. fuel return, 11. fuel supply to the injector
Control of automatic advance-injection timing is performed by quick-acting electromagnetic valve 2, which regulates fuel pressure acting on automatic advance-injection timing piston. The valve works in the pulse mode “open. close”, modulating the pressure depending on the speed of the engine shaft. When the valve is open, the pressure decreases and the angle of advance is also reduced. When the valve is closed, the pressure increases, moving the automatism piston in the direction of increasing the advance angle of injection. The pulse ratio is determined by the electronic unit, depending on the operation mode and the temperature condition of the engine. One of the injectors has an inductive needle lift sensor to detect the moment when injection starts.
Proportional electromagnetic, torque, linear or step motors are used as actuators acting on the organs controlling fuel supply to the fuel injection valve, which serve as a direct drive of the fuel dosing device in the pumps of distribution type.
As an example, Figure 6 shows the actuating mechanism controlling the fuel supply, which uses an electromagnet 2 with a rotating core, the end of which is connected through the eccentric to the metering coupling 3. when current flows through the coil of the solenoid the core rotates through an angle from 0° to 60°, accordingly moving the metering coupling. Monitor its movement with the sensor 1.
Figure 6. Electromagnetic actuating mechanism of fuel injection pump of distributive type
1. dosing stroke sensor; 2. actuating device (electromagnet); 3. dosing clutch; 4. valve of change of angle of the injection start with electromagnetic drive
No one needs to explain. the timing of the injection is very important for diesel engines. Of course, for each speed of the engine will be optimal for a particular value of angle of advance, for example, for idling 800 RPM. it is 3 °, 1000 RPM. 4 °, 1500 RPM. 5 °, etc.д. To achieve such dependence, which, by the way, is not linear, there is a special mechanism in the housing of fuel injection pump. However it is just a piston (sometimes in literature it is called a timer), which moves inside the fuel injection pump by fuel pressure and through a special train at this or that angle turns a special washer with a wave profile. The piston will be pushed further. the wave of the washer will run a little bit earlier on the plunger, it starts moving and starts supplying fuel to the nozzle earlier. In other words, the injection advance angle depends on fuel pressure inside the fuel injection pump body and on the degree of wear of the wave profile of the washer. There is usually no problem with fuel pressure. Except if the fuel filter gets clogged, the reducing valve plug gets jammed or the feed pump blades (inside fuel injection pump) get stuck.
All these problems are pretty rare and easy to figure out. You can easily and unambiguously assess the condition of the fuel filter if you switch the engine to external power, i.e. place a plastic bottle with diesel fuel under the hood of the engine, and disconnect the pipes of fuel injection pump and “return” from their regular places and drop it into this bottle. After that start the engine and check its work. It is even possible to drive a few kilometers. If there is no change in the engine behavior, it means that the fuel filter and everything located further to the fuel tank is serviceable. By the way, if you add 30-50% of any engine oil to the fuel bottle, the fuel injection system will be forced to supply thicker fuel (mix of diesel with oil). And if there is some wear in the fuel injection pump (for example, plunger pairs), this wear would affect to a lesser degree, and the engine would run better. For example, it is very difficult to start the engine when it is hot. It is often caused by the insufficient amount of fuel that is pumped due to the wear of the main plunger pair. And if with thick fuel this defect (hard starting) almost disappears, you can confidently take off the fuel injection pump and change its worn pair. Although in this case it is usually necessary to change everything in the HPF, and it is easier to throw it away than to fix and then adjust. However, this has already been mentioned above.
Condition of the reducing valve (may be in a wedged state) and the feed pump can be assessed using the manual fuel pump. If the engine runs differently after you start pumping with the hand pump running, t.е. If you are pumping manually, it means either the valve or the pump is faulty. The pressure reducing valve is easy to remove without removing the fuel injection pump and check. Only on most diesel engines you need to remove the angle of the bracket with a thin chisel, after which the head of the reducing valve becomes accessible for a special wrench. By the way, this reducing valve can also be unscrewed with a long bead (chisel), without using a wrench.
All seals there are made on rubber rings (toriqs) and do not require tightening. If the valve is intact and the plunger is not wedged open, the feed pump should be suspected. Provided that when you pump the fuel the engine runs smoother. But if during the engine operation the fuel with air bubbles flows out of the mowing line of the overflow (return), it is necessary to eliminate the air drainage first of all. Because if there is air inflow, it is difficult to create required pressure in HPF, even with a completely serviceable feed pump. But the problem with air suction is a separate topic. Here we just want to point out that the air inflow, even with an external supply, t.е. when the fuel canister is above the HPF, it is possible through the packing of the HPF and through not tightness of the central plug on the cast iron part of the HPF. This plug is used for fine setting of HPF on the fuel feed angle (it is unscrewed, the micrometer head is installed and the plunger stroke is measured, this procedure is described in almost all repair manuals for HPF). With a fully serviceable fuel injection pump, even if it was previously bled, after 10 minutes of engine operation in the mowing line overflow of air bubbles are absent.
So, the injection advance angle depends on the engine rpm. For fuel economy, high power and environmental reasons it would be better if this advance angle could be varied according to other engine conditions, such as engine load, boost pressure, temperature etc. But only with an electronically controlled HPF it is possible to take all these conditions into account completely. The conventional mechanical ones only take into account the fuel pressure in the HPF housing and, on the more modern units, the engine coolant temperature. The piston in the lower part of the fuel injection pump moves according to the fuel pressure and through a special steel “finger” slightly turns the profile washer (the same washer is forcibly turned by the lead from the warm-up mechanism). As a result, the wave projection of the washer will run over the ram earlier and the ram starts its movement earlier. This whole system was calculated and made at the factory and more or less coped with its duties. Before heavy wear and tear occurs. It became intensive because fuel without lubrication (our “dry” winter fuel as well as kerosene almost does not contain heavy fractions that provide lubrication of all rubbing parts), fuel with air and just dirty fuel (with abrasive) started to flow into fuel injection pump. However, common old age does its job too. As a result the shoulder on the washer causes the ram to run a bit later on the plunger and the latter starts moving a bit later. In other words, it’s a late injection. The beginning of this phenomenon looks like this. The engine idles and shakes a little bit because of different wear of injectors. Let’s give it more rpm. At about 1000 rpm, the engine stops shaking and sort of freezes. runs smoothly. smoothly. And then go up in rpm. Suddenly, in the 1500 to 2000 rpm range, the shuddering begins. These shuddering movements can occur either with a smooth, but intense, or a slow rise in rpm. During shaking, blue smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe. When the engine is fully warmed up, the shaking around 1500. 2000 rpm disappears. This is at the very beginning of the defect development. Then the jolt does not disappear even after the engine warms up. Exactly the same shaking occurs, if you raise the injection pressure at the injectors. In this case, if the fuel injection pump is worn, you will also get late injection. We get rid of this phenomenon by turning the housing of the fuel injection pump on an earlier injection. Sometimes it is necessary to turn the fuel injection valve almost up to the stop. But before you do that, listen to the engine. When a diesel engine has too early injection it starts to work more harshly (they also say that it has knocking valves). If you make sure that at about 50-100 rpm before the beginning of the shaking this harsh component in the acoustic background of the diesel engine disappeared, it means that it is necessary to turn the fuel injection pump. Here you should notice that at worn diesel engines the piston-cylinder gap is very big, so they start working stiff even with an absolutely correct advance angle of injection. Using stroboscope to set the lead in our case is not quite justified. Let us not talk about the fact that stroboscopes more surely catch with their microphone the knock of an already severely worn injector. If the injector is in decent condition, and the fuel line is properly secured, the strobe light tends to malfunction. To set the lead with a stroboscope is possible at idle running. This advance is given in the technical documentation. But the wear in the fuel injection system is not uniform. And very often setting the timing advance by the mark with a stroboscope at idling speed, we do not get rid of the jolting at RPM, caused by late fuel delivery. That’s why we recommend to set the advance by ear. With the wear that we have diesel engines in operation, this is a more acceptable way. This is the only way to compensate for the late injection, caused by low fuel pressure in the fuel injection pump housing due to the feed pump wear. It is almost the same as the ignition advance setting for petrol cars. You can set the advance of ignition only at idle speed with the help of devices (and the other is not offered by the repair manuals), but because of a fault, for example, a centrifugal regulator, the machine will not go. It is clear that it needs to be repaired or replaced. But by turning the tumbler you can set an acceptable ignition advance angle by ear. The only difference is that the criterion for the correct timing of gasoline engines is detonation noise and engine output, and for diesel engines. the shaking, smoke and engine noise.
As mentioned above, most of the problems with the fuel injection pump are caused by all kinds of leaks. For example the plunger is worn out, leaks, so it doesn’t build pressure. And if you change the fuel to a thicker one? Then the increased gaps in the mating parts would sort of become smaller. And the fuel injection pump will work as if it had no wear at all. It is very easy to make the fuel dense. Add, as mentioned above, any engine oil to it. Of course, you don’t want to drive like that. it is too expensive fuel (and it is troublesome to prepare thick fuel all the time). But this method is useful for checking the condition of fuel injection pump (as well as for the successful sale of a very used car at the bazaar). In the cold season, due to natural laziness, in order to make the fuel thick, we simply cool the HPF. For example, a car with a diesel engine comes in complaining that it does not start if it stands for five minutes, but the engine is still hot. We start this car (really sometimes we have to twist the starter for about 30 seconds), warm it up for about 10 minutes and then turn off. After that we open the hood and use the snow to cool the HPF. For the same 5 minutes. If after this operation the engine starts better than the first time, it is already possible to talk about heavy wearing of the fuel injection pump. Of course, both of these tricks (with thick fuel and with cooling the HPF) are not described in the factory engine repair manuals and, therefore, they cannot be considered very scientific. Those manuals measure the volume of fuel supply at startup (there is such a parameter in the technical data. the volume of supply at 200 rpm) and to check this parameter at home is also not difficult. For this you need to unscrew all glow plugs and remove the tube from one injector. Then put on this pipe a casing of disposable medical syringe and twist the engine with the starter. Naturally, counting the “squirts”. 200 “pushes”, it is certainly a lot. 50 is enough, and then compare the result with the technical data. In this case, you can assume that the injection volume at 200 rpm for all Japanese diesels, if they have the same volume, will be the same. If your engine volume is slightly different, it’s not difficult to make a proportion with the diesel volume you have the data for. We do all this also when a hot engine starts badly, though practice shows that it is possible to check even simpler. Using snow and engine oil. In other words, if the operation of fuel injection unit with thick fuel becomes more acceptable, it is necessary to check the injection volume. It is better, of course, to do it all at the stand (there one can check all operational modes of HPF), but in starting mode (t.е. at 200 rpm) check can also be done in the garage.
So, if the diesel engine has a shaking at 1500. 2000 rpm, also accompanied by a blue exhaust, it is necessary to repair the fuel system. And in particular, make the fuel injection earlier. For this purpose, in the simplest case, it is necessary to turn the fuel injection valve on an earlier injection.
Kornienko Sergey© Legion-Autodata Diagnostician d. Vladivostok