Modification Of The Screwdriver Charger
Modification of the screwdriver charger
14V. Even if we take into account that the battery serves as the smoothing capacity after the diode bridge, it turns out: 14×1.41421356 = 19.7V. That is already a little more than necessary.
The right side of the circuit: resistor R23, the final discharge voltage is adjusted: 12.48V, (or 10.4V for a 12V screwdriver, 14.56V for the 16.8V version of the screwdriver and 15.6V for the 18V screwdriver). The additional discharge mode is started with the START DISCHARGE button.
At the end of the discharge, the circuit automatically switches first to the accelerated charge mode with a current of 1.5A (1C), with a limitation of the accelerated charge time of 90 minutes (in case of a faulty battery, since the estimated battery charge time is 1 hour 15 minutes), monitoring the temperature using a thermal switch installed in the battery and control of the end voltage "-ΔV", and then switches to the mode of "drop" charging of the battery.
T.K. The transformer from the old charger is not suitable for the new circuit, it has been disposed of.
An external 25V power supply is used for power supply.
Please note that if the design is repeated, the power supply voltage must be 1.9V per cell, plus 2V for the microcircuit to function normally. THOSE. For 12 Volt screwdriver 21 V, for 14.4 V. 25V and for 18V = 30V. Or 30V for a universal charger. In this case, the jumpers must be brought out and switched depending on the battery used.
After working in the screwdriver, the battery is inserted into the charger, the "START" button is pressed, the battery begins to discharge again for 15.30 minutes, which indicates that there is still energy in the battery, and then switches to accelerated charge. (red LED in the diagram).
Connecting the charger to the battery according to the above diagram.
20.09.2011. A small modernization of the circuit was made: Instead of a discharge resistor, a relay was installed (any for 12V, for example, a car, with winding resistance
100 ohm), which, through a normally closed contact, disconnects the charger from the power supply for the time of battery re-discharge.
27.09.2011. A small modernization of the circuit was made: the thermal disconnector was used as intended for emergency termination of the accelerated charge in the event of heating of the batteries.
Commissioning 05/15/2011, is actively used in the installation of a metal profile fence at a summer cottage, which is not yet electrified.
Of the pros: 1. Reasonable price. 2. Good and sufficient torque to tighten the screws. 3. Convenient to use. 4. Very prompt support service, after writing a letter with my suggestions and comments. The answer was received within a couple of hours. They thanked for the comments and promised to arrange the supply of spare batteries within a month, as well as pay attention to the chargers. This encourages and arouses respect and an absolute plus for the ZUBR brand. 5. The fact that the battery case is large and suitable for the 18V version of the screwdriver has found its advantage: the screwdriver stands perfectly on the battery and does not fall. It turned out to be very convenient. 6. Like a drill, the RPM is not high, but sufficient to keep the drill from overheating. 7. Convenient case. 8. In the summer, it became possible to purchase additional batteries. (see below photo) P.S. 09/12/2011 8. Compared with the "STERN CD03-168B" screwdriver. The ZUBR ZDA-14.4-KN screwdriver is much better. The reducer in the "bison" is quiet, the cartridge does not dangle, the heating of the motor is barely noticeable. 9. The plant has launched the production of a pulsed universal charger for screwdrivers, at the request of the plant I tested it, I liked it. Really high quality and versatile, according to the factory, at least the sample that I disassembled and tested, I recommend to everyone. The only problem. There is no pre-discharge device, but this is easily solved by an external "extra-discharge device". Of the minuses (critical): 1. An ineffective charger included in the kit, without modification, will lead to a premature decrease in battery life.
The rest of the disadvantages disappeared with a deeper acquaintance with the screwdriver market and comparison with this model.
P.S. 09/12/2011 It’s already September. Full cycles of charge discharge at least 90 times (every day 4 batteries in the evening after drilling work, at the weekend charge from 2 batteries connected in series from UPS). The decrease in the battery capacity of the screwdriver is not noticeable. So the reliability of "Zubr" is at its best, in vain I was pessimistic.
| The printed circuit board turned out like this. (this is the old version, where a resistor was used as a discharge device, in the new version, according to the diagram, instead of a relay resistor) | On the back side. | ||
| Pre-assembly (a relay has already been added, but a very hot discharge resistor has not yet been removed). | The transformer has been removed; a pulse source will be installed in its place in the future. Contacts for the battery are installed on a special board, and the charge controller board fits into the slots where the LEDs used to pass. | ||
| This is how the resulting filling looks like. | It turned out compact, but the heating of the unit is strong. | ||
| Sliding contact option board. | How it works: Install the battery. Press "Start Discharge", the battery begins to discharge up to 1.04V per cell. (Blue LED) | ||
| After the end of the additional discharge, the circuit switches to the accelerated charge mode. |
The red LED indicates the boost charge mode, green. Nutrition.
Uncontrolled charging voltage and current is still half a trouble, with such a charger it is not far from the explosion of the elements.
Well, the "treatment" is standard: We throw out the transformer. It gives 8 volts under a load of 1.5A, a scarf with an LED is also in the trash. We leave only the case with contacts.
And in the free space we install the already prepared board (see above), not forgetting to make adjustments with jumpers (see the diagram) and replacing the resistor R19.
06/01/2011 The initial version of the page was written. 09/05/2011 additions were made. On 13.09.2011 it was decided to completely rewrite the page. 09/27/2011 final revision of the electrical circuit of the charger. (use of a thermal contact in the temperature measurement circuit of the microcircuit) © All rights to this circuit design belong to the author. When reprinting, the link is required.
Repair of power sources
Rechargeable batteries do not actually have complex spare parts, as they are assembled from the simplest charging cells. In order to decide on the repair, you need to open the source and check for damage. Tools and materials that will be needed when performing repairs:
- Multimeter.
- Screwdriver.
- Electrical contact cleaner.
- Insulating tape.
There are times when the coil of the cordless screwdriver is defective and, therefore, overheats the device. The insulation melts easily, the batteries fail and the cordless screwdriver cannot be used. A technical error cannot always be determined by visual inspection and the tool needs to be disassembled.
Sequence of operations:
- Disconnect the tool from the electrical outlet.
- Use a rag, sandpaper or electric contact cleaner to clean the contacts between the power handle and the charger.
- Plug in the power supply several times and make sure it is functioning properly.
- Check instrument at DC output. Set the multimeter to 25 DCV scale. Plug it into an electrical outlet.
- Touch two of its probes to the corresponding contacts (and.). If the meter reads zero, swap them.
- The DCV output should be near or slightly above the rated power of the source. That is, at 9 VDC, the device should show no more than 10 V.
- Check source at AC output. Set the multimeter to 25 ACV scale. Touch the two probes to the contacts. If there is no reading, the transformer is faulty. Match it for replacement with equal denomination and size.
- Check the battery. Charge the battery fully. Set the instrument on a DCV scale greater than the rated power of the battery pack.
- Touch the red probe to the terminal, and the black probe to the terminal and measure.
- Replace the battery if the reading is 1 volt below the rated power.
Drill recovery
Working under increased stress and in a dirty repair environment, the screwdriver can break. The most common causes of malfunctions are dirt or dust. Sometimes the screwdriver stops working when the copper connections on the contacts oxidize. You can repair and at the same time do the adjustment of the screwdriver with your own hands after studying the manufacturer’s instructions in the following sequence:
- Precautions must be taken before any kind of repair work.
- Make sure the electric screwdriver is not connected to power before replacing the cartridge or removing the case.
- Try turning on the tool via the battery. If it does not function, there may be a problem with the battery or power supply. Replace battery and check operation. If the electric screwdriver does not turn, it is possible that something inside is blocking the start and you will have to remove the cartridge.
- To do this, loosen the screws with a screwdriver and carefully remove the cartridge. Before you need to make sure there is a spare part to replace.
- Unscrew the housing carefully using a screwdriver. Open it, lift it up and check the device for internal defects.
- Cleaning the copper connection. If they are covered with dust or copper oxide, they must be cleaned. To do this, you can use sandpaper until the surfaces are shiny and smooth.
- Wipe off dust and copper filings with a soft cloth.
- Save the wiring diagram by taking photographs and drawing on paper. This is very important otherwise it will be difficult to assemble the wires in the same way as before the repair.
- Replacement and reassembly. Identify nodes where parts are jammed and carefully replace them.
- Assemble the screwdriver, connect the wires and install the case.
Self-charging lithium-ion batteries
Sometimes for old models of the tool it is impossible to purchase a new charger and you need to revise or make a new one yourself. For Ni-Cd and Li-ion lead acid batteries, an 18 volt screwdriver charger circuit is required. The main features of this versatile source are:
- DC voltage.
- Automatic shutdown when fully charged.
- Maximum current 5 amps, batteries can be charged normally.
- Fully customizable mode according to battery specifications.
- Low cost.
- Optimal wiring diagram. No special parts required, they are all standard and easily accessible.
- LED indicators for monitoring cut-off and charging status.
- Suitable for garages and home use.
The battery may overheat during deep charging, which should be protected by automatic temperature controller circuitry or fan cooling. List of parts for DIY screwdriver repair:
- Resistors.
- Capacitors.
- Simistra.
- Zener Diodes.
- Reducer.
Repair of the charger for the 18 volt screwdriver
The cordless screwdriver is an alternative to the conventional screwdriver for both small tasks and large home renovation projects. The tool is affordable, easy to use, and has the particular advantage of not having the usual wire from power tools. A screwdriver charger is used for periodic recharging of the batteries.
Benefits of cordless tools
Today there are many devices that successfully cope with installation work using fasteners: screwdrivers, drills, drilling machines, many of them have a charger for a screwdriver.
Small, lightweight, mobile and stand-alone screwdrivers offer the following advantages:
- Comfortable, easy-to-hold shape of the handle makes it easier to work at high speeds.
- Profitability. Many models come with useful options and attachments such as universal bits and attachments that are easy to replace for more flexibility when working.
- Energy saving design, saves energy and extends the inter-charge period.
- Increased efficiency, the tool allows you to quickly and accurately tighten fasteners in hard-to-reach places.
- High versatility. Variable speed, forward and reverse.
- Application flexibility, three-mode working range.
- Good maintainability, availability of sufficient spare parts on the market.
Wireless Power Supply Device
Battery chargers convert AC 220 V from the mains into DC. To carry out its functions, the charger has a transformer and a special printed circuit board. Batteries generate current through a chemical reaction between two electrodes and an electrolyte. Voltage ranges from 1.2 to 24 V or more, depending on battery type and amperage.
Many wireless devices are powered by a rechargeable nickel-cadmium (nicad) battery or a 20-cell rechargeable battery. Each cell provides approximately 1.2 V DC. The bags are built directly into the tool and have snap-on clips.
Modification of the screwdriver charger
A screwdriver is an indispensable tool, but the discovered flaw makes you think about making some improvements and improving the circuit of its charger. Leaving the screwdriver to charge overnight, the author of this blogger AKA KASYAN discovered the heating of the battery of unknown origin the next morning. over, the heating was quite serious. This is not normal and will drastically reduce battery life. In addition, it is dangerous from the point of view of fire safety.
Having disassembled the charger, it became clear that inside the simplest circuit of a transformer and a rectifier. Things were even worse in the dock. Indicator LED and a small circuit on one transistor, which is responsible only for the indicator to fire when the battery is inserted into the docking station. No charge control and auto-shutdown nodes, only a power supply that will charge indefinitely until the latter fails.
Searching for information on the problem led to the conclusion that almost all budget screwdrivers have exactly the same charging system. And only expensive devices have a processor controlled by smart charging and protection systems, both on the charger itself and in the battery. Agree, this is not normal. Perhaps, according to the author of the, manufacturers specifically use such a system so that the batteries quickly fail. Market economy, conveyor belt of fools, marketing tactics and other clever and incomprehensible words.
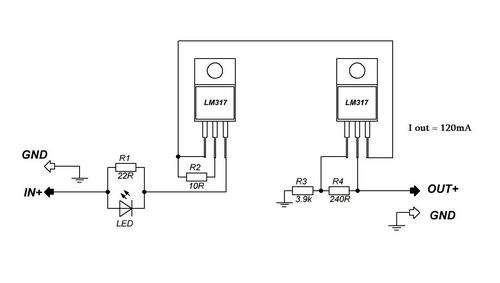
Let’s modify this device by adding a voltage stabilization and charge current limiting system. Battery 18 volt, nickel cadmium with a capacity of 1200 milliampere hours. The effective charge current for such a battery is not more than 120 milliamperes. It will take a long time to charge, but it is safe.
Let’s first figure out what this revision will give us. Knowing the voltage of the charged battery, we will set this voltage at the output of the charger. And when the battery is charged to the required level, the charging current will drop to 0. The process will stop, and the stabilization of the current will allow charging the battery with a maximum current of no more than 120 milliamps, regardless of how discharged the latter is. In other words, we will automate the charging process, and also add an indicator LED that will light up during the charging process and turn off at the end of the process.
The scheme of such a node is very simple and easy to implement. Costs just 1. Two lm317 microcircuits. The first is switched on according to the current stabilizer circuit, the second stabilizes the output voltage.
So, we know that a current of about 120 milliamps will flow through the circuit. This is not a very large current, so there is no need to install a heat sink on the microcircuit. Such a system works quite simply. During charging, a voltage drop is formed across the resistor r1, which is enough for the LED to light up and as it charges, the current in the circuit will drop. After a certain amount of voltage drop across the transistor, an insufficient LED will simply go out. Resistor r2 sets the maximum current. It is desirable to take it for 0.5 watts. Although it is possible and 0.25 watts. At this link you can download the program for calculating the microcircuit 18.
This resistor has a resistance of about 10 ohms, which corresponds to a charging current of 120 milliamps. The second part is a threshold node. It stabilizes the voltage; the output voltage is set by selecting the resistors r3, r4. For the most accurate setting, the divider can be replaced with a 10 kilohm multi-turn resistor.
The voltage at the output of the unremade charger was about 26 volts, despite the fact that the test was carried out with a 3 watt load. The battery, as mentioned above, is 18 volts. Inside there are 15 1.2 volt nickel cadmium cans. A fully charged battery has a voltage of approximately 20.5 volts. That is, at the output of our node, we need to set the voltage within 21 volts.
Now let’s check the assembled block. As you can see, even with a short-circuited output, the current will not exceed 130 milliamperes. And this is regardless of the input voltage, that is, the current limiting works as it should. We mount the assembled board into the docking station. As an indicator of the end of the charge, we will put the native LED of the docking station, and the board with the transistor is no longer needed. The output voltage is also within the specified range. The battery can now be connected. The LED lit up, charging has started, we will wait for the completion of the process. As a result, we can say with confidence that we have definitely improved this charging. The battery does not heat up, and most importantly, you can charge it as much as you like, since the device automatically turns off when the battery is fully charged.
In another article about reworking a transformer.
Charger circuits for screwdrivers. Effective charger circuit for screwdriver
In the process of using a cheap Chinese screwdriver, recently purchased, it was found that the standard charging is weak. Accordingly, I needed a charger circuit for a screwdriver that would work stably. And then the native, Chinese, charger slowly charged at a reduced voltage in the network and was very hot when connected to an increased voltage of 220V.
To assemble a homemade charger for my instrument, I used a circuit that has already been repeatedly tested, the heart of which is a composite transistor KT829. This design has already been used in practice by many people.
Depending on the voltage on the battery, the charging current passing through it is regulated by KT361, the collector voltage of the transistor controls the charge indicator, and the KT361 itself controls the operation of the composite transistor. The LED is on during the charging process, and as the charging current decreases, the LED gradually goes out.
The maximum charging current is limited by a 1 Ohm resistor. The required voltage on the battery determines the moment when the charge is full, the process is completed, and the charging current decreases to zero. The variable resistor sets the charge threshold and after adjustment, then it is replaced with a constant resistor of the required resistance. The charge threshold itself must be set slightly higher than the value that provides maximum capacity charging.
In addition to transistors, of course, any charger circuit for a screwdriver contains a transformer. In this case, a transformer was used in the secondary winding of which the voltage is 9 volts and the current is 1A, the brand is TP-20-14. This transformer was removed from an old "Elektronika-409" black and white small format TV. You can find a similar transformer by digging it out of another representative of the "TV and radio dinosaurs".
So, now it remains to neatly mount the ready-made device for charging the screwdriver into any plastic case with suitable dimensions. The improved screwdriver charger circuit presented in this article is reliable and works very well. A year of work without failures demonstrated the absence of flaws, all this time, the screwdriver from this device was charged reliably and quickly.
Standard and individual characteristics of the Interskol charger
- Interskol chargers use transceivers with increased conductivity. Their maximum current load reaches 6 A, and in new models it is even higher. The standard charger of the Interskol screwdriver uses a two-channel microcircuit, 3 pF capacitors, pulse transistors and open-type tetrodes. Current conductivity reaches 6 μA, with an average battery power of 12 mAh.
- Quite often, the Russian manufacturer Interskol uses a battery charging circuit with IRLML 2230 transistors. In this case, a three-channel type microcircuit and capacitors with a capacity of 2 pF are used in 18 V chargers, which tolerate network loads well. The conductivity index in this case reaches 4 μA. When choosing a screwdriver, you need to take into account its power, which affects its service life. The higher the power rating, the longer the tool will last.
Power supply elements
The battery is the most expensive part of a screwdriver and accounts for approximately 70% of the total cost of the tool. If it fails, you will have to spend money on purchasing a practically new screwdriver. But if you have certain skills and knowledge, you can fix the breakdown yourself. This requires certain knowledge about the features and structure of a battery or charger.
All elements of a screwdriver, as a rule, have standard characteristics and dimensions. Their main difference is the value of energy consumption, which is measured in A / h (ampere / hour). The capacity is indicated on each element of the power supply (they are called "banks").
"Banks" are: lithium. ionic, nickel. cadmium and nickel. metal. hydride. The voltage of the first type is 3.6 V, others have a voltage of 1.2 V.
A defective battery is detected by a multimeter. He will determine which of the "cans" is out of order.
Standard wiring diagram for charger
The basis of the standard circuit is a three-channel type microcircuit. In this version, four transistors are attached to the microcircuit, very different in capacitance and high-frequency capacitors (pulse or transient). To stabilize the current, thyristors or open-type tetrodes are used. The current conductivity is regulated by dipole filters. This circuitry handles network overloads easily.