Gas cutting of metal with propane and oxygen
Types of gas cutting of metal
The technologies of the modern world have made great strides forward. Now anyone can cope with the gas cutting procedure, because it is much easier than gas welding, so almost no skills are required for admission. The main thing to understand is gas cutting technology. and more propane torches are used and require a combination of propane and oxygen to work with them. Such a mixture provides the required temperature, due to which, gas cutting of metal is carried out.
How is cutting done?
Cutting is performed with simultaneous heating. For this very purpose, the torch tip has 3 nozzles. The lateral ones are used to supply the heating mixture, and the thinnest nozzle is located in the center, through which oxygen is supplied under very high pressure.
If we talk about pressure, then it can reach 12 atmospheres, this power is enough for a person who puts his hand under the stream of air to damage his skin. When this jet is ignited, metal structures are cut.
With this cutting method, a flux is formed, which is scattered by the flame to the sides, and if through cutting is performed, then it is burned through the entire thickness of the material. This makes cutting metal much better than electric cutting. After all, the resulting seam is very neat.
If we go back to metals, the melting point of which is below 600 degrees Celsius, then cutting them will not work due to the removal of the upper layer of metal, which will be repeated until the very end of cutting. In order to still carry out cutting, it is required to use mobile heaters. These are small canisters of compressed gas with a nozzle.
Special moments in cutting
Metal cutting technology says that there is no need to rush to open the valve of the propane cutter, because in this case, you expose yourself to the danger that can arise from the interaction of oxygen with a heated metal. To exclude a back blow of the flame, it is required to remove the oxygen stream, strictly following the angle of inclination of the burner.

At first, it is equal to 90 degrees, after which a small deviation is made, by about 6 degrees, in the opposite direction to the movement. If you are cutting thick metal, then the deviation can increase up to 70 degrees.
It is important to remember that the cutting process for metal must occur at the same speed, which is selected by the visual method, for example, you can estimate the speed of spark spread.
At optimum speed, sparks are emitted at a 90 degree angle. If the sparks are flying in a direction other than the direction of travel of the torch, the cutting speed is very slow. Informs about high speed if the angle of emission of sparks is less than 80 degrees.
The thickness of the metal plays an important role, because if the thickness of the metal is quite large, then it is impossible to monotonously move the cutter until the moment when the sheet is cut across the entire thickness. Towards the end of the cut, an increase in the angle of inclination by about 15 degrees is required.
During the procedure, there should be no prolonged pauses. If the work was still stopped at some point, then the cutting should be started from the very beginning and a new starting point should be chosen.
The end of the cut must be followed by the following actions, in this order:
- stopping the supply of cutting oxygen;
- stopping the supply of regulating oxygen;
- propane shutdown.
Pros and cons of flame cutting
This cutting method has many advantages:
- Flame cutting allows you to cut thick material. And also with the help of it, you can make a neat cut along the stencil. It is simply impossible to achieve the accuracy of the work when using an angle grinder, and if it becomes necessary to cut a hole to a certain depth, then only gas cutting will cope with this.
- Flame cutting requires a torch that is light and lightweight. This allows you to achieve comfort during work, and if you compare the cutter with gasoline counterparts, the difference is enormous. Gasoline cutters make a lot of noise, they are difficult to make accurate cuts due to their heavy weight, and strong vibrations force the operator to apply force when cutting. Oxygen pressure saves energy.
- Gas cutting allows you to speed up the cutting process by almost 2 times when comparing the results shown by gasoline counterparts.
- The cut accuracy is worse than that of an acetylene cutter, but much better than that of a gasoline and angle grinder.
- Propane is a very cheap gas. Its use is beneficial in cases where a large amount of work is required.
Alas, there are also disadvantages, however, there are much fewer of them, or to be more precise, one is a limited range of metals that can be cut.
For example, flame cutting of metal with propane and oxygen cannot cut steel with high carbon content. Therefore, the use of this type of cutting is justified only for low and medium carbon steel.
This limitation arises due to the fact that the melting point of high-carbon steels is equal to the burning temperature of the torch, therefore, when cutting, the material melts and does not allow oxygen to get inside.
Hence the rule: for successful cutting, the burning temperature of the cut metal must be less than its melting temperature.
Cutting process
Before starting cutting, you need to remove rust from the metal.
When cutting, the workpiece must be positioned so that the outgoing jet can easily pass through it.
At the very beginning of the procedure, the surface of the material is heated to the temperature of the metal burning. Oxygen and combustible gas are used. After reaching the desired temperature, oxygen is supplied, which will ignite, due to contact with a hot surface, and it is he who will cut.
At this point, it is important to achieve the continuity of the oxygen supply, otherwise, the flame will go out and the surface will quickly cool down, and then it will have to be reheated.
There is a clear correlation in the cutting procedure. the purer the oxygen used, the better the cut quality. And also sometimes a situation arises in which the oxygen jet abruptly cuts into the metal and the cutting power drops, and the curvature of the flow begins. In order to avoid such a situation, you need to slightly tilt the jet.
It is important to understand that the jet has a conical shape and expands closer to the bottom. Because of this, the width of cut increases as the end of the cut is approached and dross forms.
You can correct the situation by increasing the power of the cutter, but do not get carried away too much, if you overdo it, then dross will appear on the upper part of the metal.
The quality of the cut is strongly influenced by the oxygen pressure. High pressure inevitably leads to a bad cut, and the oxygen consumption becomes enormous. Low pressure will not allow cutting through the metal and it will be difficult to remove oxidation. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the average indicators, which are individual for each metal, and regulate the oxygen supply from the oxygen cylinder.
Required equipment
In order to use a gas cutter, you need to have at least one propane and oxygen cylinder, hoses designed for high pressure, a cutter. Each cylinder comes complete with a reducer, with which you can adjust the gas flow. The propane tank is reverse-threaded, so it is not possible to use another reducer on it.
There is not much difference between different metal cutters. All have 3 gates:
- one for propane supply;
- the second is for regulating oxygen;
- third. cutting oxygen.
All oxygen valves are blue and for propane they are red. The metal is cut with a jet of flame.
The gas cutter can cut metal with a thickness of up to 300 mm. The device is very easy to repair, since many parts of the device are replaceable.
Safety engineering
You need to understand that cutting metal with gas is a process that even a beginner can master, but this process does not become less dangerous. Therefore, training can only be carried out under the supervision of an experienced specialist.
To carry out work on cutting metal, you should adhere to the following safety precautions:
- Good ventilation must be provided in the work area.
- Remove all hot substances within 5 meters of the cutting site.
- Work can only be carried out in special clothing: protective mask, fireproof clothing.
- Do not direct the flame towards the gas source. Its direction should be diametrically opposite.
- During the operation of the cutter, it is forbidden to step on the hoses, wiggle them, physically influence them in every possible way.
- During a break, you need to extinguish the flame at the torch, tighten the valves on the gas cylinders.
Effective and safe cutting can only be achieved by following all these rules, which are difficult only at first glance.
Gas cutting of metal with propane
Gas cutting of metal with propane is the most effective and popular type of cutting, since it does not need a special room, the presence of a grounding cable, moreover, it remains mobile when moving. Propane gas is used to heat the metal, and oxygen separates the metal. The heating temperature during gas cutting of metal with propane is 1000. 1200 0 С, this allows the jet to ignite when oxygen and metal are combined. When cutting with propane, the seam remains fairly clean than when cutting metal electrically. The flux during cutting is ejected by the heating flame, but it can also burn through the entire metal. It should be borne in mind that gas cutting of metal with propane is not used when cutting metal with a melting point below 600 0 С, otherwise the upper layer of metal will be removed.
Metal cutting with a modern type gas cutter takes place at a pressure of 12 atmospheres. There are two tubes in the handle of the cutter, built into the handle, three of them are fed to the nozzle. Propane is supplied to two of them, and oxygen through the third. Oxygen is consumed depending on torch model. Cutting metal with a gas cutter P1. 01 per hour of work uses 10m 3. oxygen and 1m 3 propane. Torch model P2.01 consumption is much higher. This cutter can cut low-carbon and medium-carbon steels, cast iron. High carbon ones prevent oxygen from penetrating deep into the metal to burn it through. Non-ferrous metals. aluminum, copper, as well as their alloys are also not amenable to flame cutting.
Cutting metal with a gas cutter is successfully used when cutting thick metal, cutting discs of large thickness, burning out a blind hole of 20-50 mm., The work is done much faster than with other cutting methods, propane is also cheaper than gasoline and other combustible gases.
Leave your comment cancel reply
Waterjet cutting is a process of exposure to a water jet with particles
Surface treatment
This method is produced with a gas-oxygen jet with the aim of actually creating grooves in order to impose a weld seam, as well as eliminate defects in castings, welds and forgings.
The difference between surface treatment and separation cutting of metal is that the cutter mouthpiece is located perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece (during surface treatment, the angle is 35 ° or more). Nearly all surface cutting with oxygen results in a groove that is characterized by the width, curvature and depth of the surface.
When gouging the surface and further processing rather large surfaces, the groove comes out of a large length, sections along the length. When cutting, the cutter is moved by means of a mechanism.
Removal of material flaws, as well as gouging of grooves is performed using a manual method. In the surface treatment of metal parts, special torches for oxyfuel cutting with increased flame power and a special tip are used. The torch mouthpiece has six concentric flame (preheat) holes instead of an annular channel for cutting oxygen.
The angle between the treated surface and the axis of the mouthpiece is within 15-25 degrees. taking into account the distance from the end of the mouthpiece to the treated surface 1-2 millimeters (no more). It should be noted that the cutter has an elongated handle. During turning of cylindrical products, the cutter is placed in an upright position on the support, while the product is rotated in the centers.
Oxygen cutting: types and subtleties of the work process
Separation cutting
In our time, separative oxygen cutting of metal (possible with propane) has earned special distribution. Oxy-fuel cutting technology allows the technique to be used almost everywhere. Oxygen treatment is performed using a jet perpendicular to the surface (cut) or inclined (for beveling the edges).
Oxygen cutting begins with edge heating. When the required temperature is obtained (1050. 3000 degrees C. ignition temperature), a jet of cutting oxygen is launched (oxygen consumption begins), after which the cutter begins to move (using a mechanized drive or manually).
Cutting the edges of metal sheets with oxygen in preparation for welding can be done with three torches at the same time. It is worth paying attention to the fact that in this case, both edges get the necessary X-shaped bevel overnight. The procedure (oxygen consumption and cutting application) is quite productive, since the work of inclined cutters is carried out in light conditions, heating a metal part heated by a vertical (leading) cutter. Oxygen consumption is an important point that requires attention.
Note that the speed of separation cutting with propane using oxygen in the case of using a special cutter shape can be significantly increased, but it will be necessary that the cutter directs the cutting stream at an angle to the plane of the metal sheet being cut, and not perpendicularly. With the lengthening of the path of passage of the jet in the metal part, heating of the edge is observed, which arises as a result of the movement of molten slag along it. At the same time, the productivity of work increases several times.
Oxy Propane Torch
In order to separate metal parts with high alloying impurities into parts, oxygen-flux cutting is used. It should be noted that cutting alloy steels or cast iron, for example, containing chromium in the composition at the level of 7%, using conventional oxyfuel cutting methods is almost impossible.
When cutting with oxygen (as soon as the cylinder is consumed), oxides are formed, which have high melting points, cause the slag to thicken, and are also disgustingly removed and create obstacles to oxidation of the metal layers (during cutting) lying underneath. During the application of oxygen-flux cutting of metal, a powdery flux is fed from a special hopper into the oxygen stream (cutting). Don’t forget about oxygen consumption.
Oxygen cutting
Oxygen cutting is based on the property of the metal to burn under the action of an oxygen jet, as well as on the removal of the resulting combustion products by the jet. Cutting the material begins with heating the metal at the beginning of the cut by means of the heating flame of the cutter until the ignition temperature of the metal is formed in the oxygen stream.
After that, cutting oxygen is supplied, which, in turn, leads to the continuous formation of metal oxides throughout the entire thickness, after which the cutter moves along the mowing line of the cut. Oxygen cutting is applied only to those metals and alloys that, when exposed to oxygen, have the following qualities:
- The temperature is lower than this indicator when they melt;
- The melting point of metal oxides that are formed during cutting is lower than the melting point of the metal itself;
- The amount of heat generated by combustion in oxygen is large enough to maintain a constant oxy-fuel cutting;
- Slag resulting from cutting must be fluid and blown out easily enough from the place where oxy-fuel cutting was used;
- The thermal conductivity of alloys and metals is not too high.
Oxygen cutting
There are several types of oxygen cutting. These varieties depend on the shape, material of the part, and also on the place of the cut.
The first group. Separating oxygen cutting (straight, shaped, cutting with the use of oxygen with beveled edges for welding):
- High-speed oxygen cutting;
- Normal oxygen cutting;
- Oxygen-flux.
Second group. Surface treatment:
- Surface gouging;
- Air gouging;
- Turning.
The third group. Drilling (or burning holes);
- Oxygen spear;
- Regular jet.
Fourth group. Special oxygen cutting procedures (electrooxygen, underwater oxygen cutting, etc.).
Now you need to deal with all the groups that relate to such a concept as oxygen cutting.
Drilling
Holes are made with a gas cutter. It is also possible to pierce holes in the whole metal surface or starting from an initial small hole drilled for initial heating of the edge.
In fact, such a procedure is oxy-fuel cutting, directed along a small diameter circle. Burning through may result in an irregular hole. The hole can be pierced when there is a small metal thickness (no more than 8 millimeters).
To burn large-diameter holes in blanks and castings in the metallurgical industry, a type of process called a sharp spear is used.
Special Oxygen Cutting Processes
This variation is also one of the ways of the concept, better known as oxyfuel cutting. It is widely used in diving or during the repair of parts of a ship under water. Also, the method finds application during hydraulic works, disassembly of sunken ships.
A gas-oxygen flame, the consumption of which requires attention, tends to burn perfectly under the water column, but provided that a certain protective shell is created around it. In turn, the protective shell, which facilitates oxy-fuel cutting, is the blown air, combustion products (flow rate). In the role of a combustible gas, the consumption of which is quite high, during the underwater cutting, it is mainly played by hydrogen. Acetylene can also be used, however, only at shallow depths (up to 10 meters).
When cutting metals underwater, liquid fuel is used: benzene, gasoline, etc. The underwater cutting torch provides three mouthpieces: oxygen is supplied through the first mouthpiece (inner), a hot hydrogen-oxygen mixture passes through the second, and the third mouthpiece (outer) serves as a cap to form a protective air layer.
In accordance with this, hoses from three cylinders are supplied to the cutter: oxygen, air, hydrogen. During underwater cutting, the oxygen pressure is set in the range of 5-10 atmospheres (sufficient flow). The ignition of the mixture, as well as the further regulation of the flame, were carried out in air. Today, special underwater electric low voltage lighters are used for this. These lighters are powered by alkaline batteries.
Recently, the oxygen-arc process has become widely used in underwater metal cutting, during which the metal part is literally burned with oxygen if the flow rate is sufficient. In this case, heating is carried out by means of an arc. A tubular steel electrode is also used, into the inner part of which volumes of oxygen are injected.
The oxygen supply (flow rate) is made from the rear of the moving arc. The method involves the use of a solid carbon or metal electrode. A channel is made into the coating of such electrodes, which supplies portions of oxygen. Oxygen-arc metal cutting is often used in outdoor cutting.
Propane & Oxygen Torch Cutting Instructional Video
However, productivity and cut quality are lower than those of conventional oxy-fuel cutting. Oxygen-arc action on a metal part is advisable for those alloys and metals that are not amenable to oxygen cutting in the usual way. Propane is not used for this purpose.
It should be noted that it is important to comply with safety regulations for flame cutting and other oxygen metal cutting procedures. Great attention should be paid to the explosiveness of combustible gases. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the fact that the presence of oxygen, which intensifies combustion, has every chance of contributing to the ignition of foreign materials (fabrics, paint, etc.). This is especially true for work in closed compartments of ships, boilers, etc. Therefore, before starting work on cutting, and with compressed gas cylinders, you should carefully study the necessary instructions. Handling propane and other gases is life-threatening, so be very careful when cutting and handling hazardous objects. Oxygen consumption must comply with the standards.
Nuances of metal cutting
When cutting metal, it is important to maintain the required speed. Its selection is carried out visually, for which the speed of spread of sparks is estimated.
Acetylene or Propane. Which Fuel Gas is best for you?

If the speed is optimal, then the flow of sparks will fly out at an angle of about 88-90 degrees in relation to the cut surface. In a situation where the flow of sparks tends in a direction that is opposite to the movement of the torch, it can be concluded that the cutting speed is too low. In some cases, sparks are emitted at an angle of less than 85 degrees. This is a hint that the current cutting speed is too high.
When cutting with gas, it is important to consider such a parameter as the thickness of the metal. If it has a value of more than 60 mm, then it is advisable to place the sheets at such an angle that the slags easily slide to the side.
If you have to work with a metal that has a significant thickness, then a special approach must be taken here. It is unacceptable to move the torch until the metal has been cut to its full thickness. As the cut is complete, it is important to gradually reduce the advance speed and maintain the torch tilt angle 10-15 degrees more. The cutting procedure itself should be carried out in such a way that during it there are no significant pauses. If it happened that you had to stop at a certain area, then you do not need to return to cutting at the point at which the work was interrupted. It starts from the beginning, and a new starting point is chosen.
After the end of the cut, the cutting oxygen supply must be shut off, after which the same is done with the regulating oxygen. The final action should be to turn off the propane.
Cutting metal with an oxygen-propane cutter
Gas cutting seems to be a simpler process than gas welding, and therefore even a person without special skills can cope with it. For this reason, almost any of us can learn to work with a gas torch. The main thing here is to learn the essence of gas cutting technology. In modern conditions, propane cutters are increasingly used. Working with them requires the use of propane and oxygen at the same time, since the combination of such substances provides the maximum combustion temperature.
Features of use
Such tools are not suitable for cutting high carbon steels because they have a sufficiently high melting point, which is almost the same as the flame temperature. This leads to the fact that instead of ejection of scale, which looks like a pillar of sparks, from the back of the sheet, it is mixed with molten metal along the edges of the cut. As a result, oxygen cannot reach the thickness of the metal, which is why it cannot burn through the material.
Difficulties in cutting cast iron are created by the shape of the grains, as well as the graphite between them. True, this does not apply to ductile iron. It is impossible to solve the problem if you have to deal with aluminum, copper and their alloys.
It is important to dwell on the following point: the category of low-carbon steels is represented by grades from 08 to 20G, medium-carbon. grades from 30 to 50G2. A characteristic feature of carbon steel grades is the presence of the letter U in front of their name.
Surface and shape cutting
In some situations, it may be necessary to emboss a surface by cutting a groove in the sheet. If it is decided to use a similar cutting method, then the heating of the metal will be provided not only by one flame of the torch. The molten slag will also contribute. As it becomes liquid, it will spread over the entire surface, which will lead to heating of the lower layers of the metal.
The first stage in the implementation of surface cutting is the heating of the selected area to the ignition temperature. After starting the supply of cutting oxygen, you will create a metal burning zone, and thanks to the uniform movement of the cutter, the cut line will get a clean edge. The operation itself must be performed in such a way that the cutter is at an angle of 70-80 degrees in relation to the sheet. When cutting oxygen begins to flow, the cutter is positioned so that it forms an angle of 17-45 degrees from the work surface.
To create grooves of suitable dimensions, it is necessary to change the cutting speed: to obtain a greater depth, the speed increases, and for a smaller one, it decreases. To create more depth, the angle of inclination of the mouthpiece must be increased, cutting must be done at a slow pace, while the oxygen pressure must also be increased. The width of the groove can be influenced by using the correct diameter of the cutting oxygen jet. It should be borne in mind that the difference between the depth of the groove and its width must be up to 6 times. over, the latter should have an advantage. Otherwise, you may encounter such an unpleasant phenomenon as the appearance of sunsets on the surface.
Preparation for work
Before starting gas cutting, it is necessary to inspect the device to make sure that the propane torch is in working order. Next, you need to perform the following operations:
- Preparing the cutting machine begins with connecting the hoses to it. Even before attaching the sleeve, it is purged with gas. this will remove debris and dirt from it.
- The oxygen hose must be connected to a right-hand threaded fitting, a nipple and a nut are used for this purpose. As for the hose through which the propane will flow, it is attached to the fitting with a left-hand thread. Before connecting the gas hose, it is imperative to find out if there is a suction in the cutter channels. This task can be solved by connecting the oxygen hose to the oxygen fitting, while making sure that the gas fitting remains free.
- Next, you need to set the oxygen supply level to 5 atmospheres, after which you need to open the valves that regulate the flow of gas and oxygen. Touch the free fitting with your finger. this way you will know if there is an air leak. If it is absent, you will have to clean the injector and blow out the cutter channels.
- After that, you need to make sure that the detachable connections are sealed. If it is possible to identify a leak, fix it by tightening the nuts or replacing the seals. You should also make sure that the mountings of the gas reducers are sufficiently tight, whether the pressure gauges are in working order.
Cutting features
Take your time when opening the valve on the propane torch. In this case, oxygen will ignite naturally as a result of interaction with a heated metal. By doing this, you will eliminate the risk of flames blowing back, during which a popping sound can be observed. It is necessary to slowly conduct the oxygen stream strictly parallel to the specified mowing line. It is important here not to be mistaken with the angle of inclination.
First, it is kept at 90 degrees, after which it is necessary to create a slight deviation of 5-6 degrees in the direction that is opposite to the movement of the torch. If you have to deal with metal, the thickness of which is more than 95 mm, then it is allowed to increase the deviation to 70 degrees. After the cut in the metal reaches 15-20 mm, the angle of inclination begins to increase to 20-30 degrees.
Advantages and disadvantages
Cutting metal with propane has a number of advantages, among which the following can be distinguished:
- Gas cutting is in demand in a situation where there is a need to cut metal of considerable thickness or create products according to templates that provide for the production of a curvilinear cut that cannot be performed using an angle grinder. Also, you can not do without a gas cutter, and then, as there is the task of cutting out a disc from thick metal or making a blind hole by 20-50 mm.
- The torch is a very easy-to-use tool and is lightweight. All DIYers who have had experience with gasoline models are aware of the inconvenience associated with heavy weight, size and noise. In addition to the significant inconvenience caused by vibration, the operator is forced to provide serious pressure during operation. Gas models, on the other hand, seem to be a more attractive alternative due to the lack of all the above-mentioned disadvantages.
- The use of cutting metal with gas allows you to speed up the work 2 times, which cannot be done using a device equipped with a gasoline engine.
- Among most gases, including gasoline, propane stands out at a lower price. For this reason, it is better suited for a significant amount of work, for example, if there is a task to cut steel for scrap.
- With propane cutting it is possible to create a narrower cut edge than with acetylene cutters. At the same time, the method under consideration allows you to create a cleaner cut than that which can be done using gasoline burners or an angle grinder.
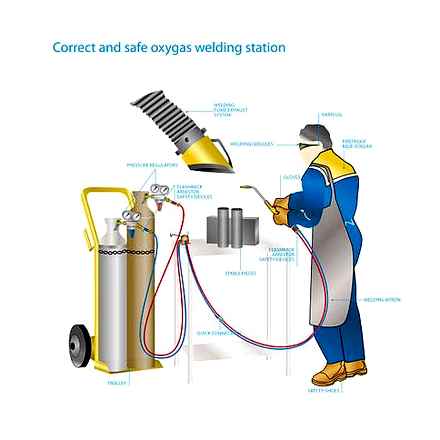
Among the disadvantages that propane cutters have, only one should be highlighted: they can be used only for a limited range of types of metals. They are suitable for cutting extremely low to medium carbon steels and also ductile iron.
Necessary equipment
As in the case of any other work, even before starting to cut metal with gas, the necessary equipment should be prepared:
- Propane and oxygen cylinder. 1 pc.;
- High pressure hoses;
- Cutter;
- Mouthpiece that must be of a certain size.
A prerequisite is the presence of a reducer on all cylinders, with which it will be possible to adjust the gas supply. It should be remembered that the propane cylinder has a reverse thread, which makes it impossible to screw an additional reducer onto it.
In general, gas equipment for cutting metal has a similar device, regardless of the manufacturer. Three valves can be distinguished in the design:
- the first provides propane supply;
- the second valve allows you to change the oxygen supply;
- the last is the cutting oxygen valve.
Oxygen valves are usually labeled in blue, and red or yellow for propane valves.
Cutting metal is provided by a jet of hot flame that acts on the metal, which is created using a cutter. When it is turned on, propane and oxygen are mixed in a special mixing chamber, which leads to the appearance of a combustible mixture.
With a propane cutter, you can cut metal with a thickness of less than 300 mm. A detailed installation is completed with elements, which are mostly replaceable. For this reason, if a particular part fails, it will not be difficult for the operator to carry out repairs directly at the workplace.
Care should be taken when choosing a mouthpiece. The key parameter that you need to pay attention to is the thickness of the metal. If you have to deal with an object that provides elements of different thicknesses ranging from 6 to 300 mm, then you will have to prepare mouthpieces with internal numbers from 1 to 2, and external numbers from 1 to 5.
Preparation for work
Before starting work, you must make sure that it is safe: there must be no traces of oil and other flammable substances on the clothes, floor, surrounding surfaces. Next, you should inspect the gas equipment for complete set and serviceability. The following steps will help you get your equipment on standby:
- Purge all high pressure hoses with gas to remove dust and dirt before connecting them. Check for leaks in the cutter passages. Attach the oxygen hose to the right-hand thread with a nipple and nut. Attach the propane hose to the left fitting;
- Check for gas leaks in the detachable joints;
- Check the serviceability of the pressure gauges. Pay attention to the tightness of the gas reducers.
Beginning of work
Oxygen consumption when cutting metal is 10 times higher than propane consumption.
- Close all the valves of the torch and set the operating atmospheres on the reducers: on oxygen. 5, on gas. 0.5.
- Open the propane bottle a quarter and light it.
- Angle the torch nozzle against a metal surface and gently open the regulating oxygen.
- Go to the flame adjustment process: alternately open oxygen and gas until the flame turns blue and a crown appears.
- Choose the strength of the flame based on the thickness of the metal.
To work, you must have
All parts of the gas equipment are standard and can be replaced in the event of a breakdown.
Cutting process
With the correct choice of the speed of movement of the torch, a stream of sparks and slag flies out of the cut straight down, while the edges are clean, there are no smudges and fusion.
If in the process of performing work your oxygen hose breaks, do not panic. Close the propane supply and then both cylinders. The flame that has disappeared during the adjustment process must be re-ignited, having previously closed the cutter valves.
Metal cutting with oxygen and propane
When it becomes necessary to work with thick metal, a gas cutter is used. It cuts the sheet metal using a hot flame jet. It is formed due to the mixing of two gases. propane and oxygen.
It is impossible to cut high-carbon metals, copper and its alloys, aluminum with an oxygen-propane cutter. The range of influencing materials is limited to low-carbon steels of grade 08 to 20G in accordance with GOST (1050-60) and medium-carbon steels. from 30 to 50G2 (GOST 1050-60).
Propane cutter cuts metal no more than 300 mm thick.
Safety in cutting and welding
The developed clear safety rules made it possible to make the process controlled, the life and health of the carvers and those around them became out of danger:
- Use of a special mask with light filters, a respirator and a protective suit.
- Admission to work of persons who have reached the age of 18 years and have passed a special course in gas business, having a certificate with a mark to carry out this type of work.
- Soaping for tightness of all connections of equipment, pipelines and fittings to prevent gas leakage.
- Use of special trolleys and stretchers to move individual cylinders. No impact of cylinders against each other during transportation.
- Do not get on the oxygen reducer, valve or hose with liquefied gas, grease, oil.
- It is forbidden to open the reducer and the valve of the oxygen cylinder with oily hands.
- Before starting work, bleed the gas / air mixture that forms in the hose through the torch. This prevents kickback into the hose and gearbox.
- Heating metal only with liquefied gas without oxygen is strictly prohibited.
Preparation for work
Before starting work, you must make sure that it is safe: there must be no traces of oil and other flammable substances on the clothes, floor, surrounding surfaces. Next, you should inspect the gas equipment for complete set and serviceability. The following steps will help you get your equipment on standby:
- Purge all high pressure hoses with gas to remove dust and dirt before connecting them. Check for leaks in the cutter passages. Attach the oxygen hose to the right hand thread with a nipple and nut. Attach the propane hose to the left fitting;
- Check for gas leaks in the detachable connections;
- Check the serviceability of the pressure gauges. Pay attention to the tightness of the gas reducers.
Cutting process
With the correct choice of the speed of movement of the torch, a stream of sparks and slag flies out of the cut straight down, while the edges are clean, there are no smudges and fusion.
If in the process of performing work your oxygen hose breaks, do not panic. Close the propane supply and then both cylinders. The flame that has disappeared during the adjustment process must be re-ignited, having previously closed the cutter valves.
Metal cutting with oxygen and propane
When it becomes necessary to work with thick metal, a gas cutter is used. It cuts the sheet metal using a hot flame jet. It is formed due to the mixing of two gases. propane and oxygen.
It is impossible to cut high-carbon metals, copper and its alloys, aluminum with an oxygen-propane cutter. The range of materials that can be affected is limited to low-carbon steels of grade 08 to 20G in accordance with GOST (1050-60) and medium-carbon steels. from 30 to 50G2 (GOST 1050-60).
Propane cutter cuts metal no more than 300 mm thick.
Beginning of work
Oxygen consumption when cutting metal is 10 times higher than propane consumption.
- Close all the valves of the torch and set the operating atmospheres on the reducers: on oxygen. 5, on gas. 0.5.
- Open the propane bottle a quarter and light it.
- Angle the torch nozzle against a metal surface and gently open the regulating oxygen.
- Go to the flame adjustment process: alternately open oxygen and gas until the flame turns blue and a crown appears.
- Choose the strength of the flame based on the thickness of the metal.
To work, you must have
All parts of the gas equipment are standard and can be replaced in the event of a breakdown.
Safety in cutting and welding
The developed clear safety rules made it possible to make the process controlled, the life and health of the carvers and those around them became out of danger:
- Use of a special mask with light filters, a respirator and a protective suit.
- Admission to work of persons who have reached the age of 18 years and have passed a special course in gas business, having a certificate with a mark to carry out this type of work.
- Soaping for tightness of all connections of equipment, pipelines and fittings to prevent gas leakage.
- Use of special trolleys and stretchers to move individual cylinders. No impact of cylinders against each other during transportation.
- Do not get on the oxygen reducer, valve or hose with liquefied gas, grease, oil.
- It is forbidden to open the reducer and the valve of the oxygen cylinder with oily hands.
- Before starting work, bleed the gas / air mixture that forms in the hose through the torch. This prevents kickback into the hose and gearbox.
- Heating metal only with liquefied gas without oxygen is strictly prohibited.