What The Puncher Consists Of
Cartridge
The hammer drill chuck is designed in such a way that the user has the opportunity to quickly change the accessory without making long interruptions in work. We are talking about two main types of cartridges:
- SDS-plus;
- SDS-max.
Tool shank for SDS-plus chuck is clamped with two locking balls.
SDS-max chucks accept tools with different shanks for more secure clamping.
What the tool can do
The following main operating modes of the punch are distinguished:
- Rotating Impact. allows you to drill into a concrete wall;
- Impact without rotation. to hammer in concrete;
- Impact-free rotation. with drill attachment allows you to drill like a drill.
Those who often work with a puncher know that in addition to drilling and chiselling walls, such a tool can be used to groove walls for wiring. Making a slab in concrete using this tool is quite simple. First, a number of holes are drilled along the marked lines. Then, with a lance or a spatula, break the jumpers between the holes. This use of a punch is atypical, but allows you to refuse to purchase additional tools.
Impact mechanism
The percussion mechanism in the construction of rock drills is of two types:
- Electromechanical;
- Electro-pneumatic.
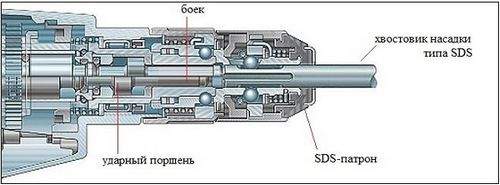
The most widespread is the electro-pneumatic version. "Drunk" (swinging) bearing and piston together make up the hammer hammer mechanism.
When the main shaft rotates, the swinging bearing makes translational movements, transferring the force to the ram of the pneumatic cylinder. The air in the cylinder pushes the piston with the striker. The working part of the chuck is exposed to the impact of the striker, the drill clamped into the chuck hits the material being processed.
What the puncher consists of
The controls are located on the body of the tool, as can be seen in the following photo:
The internal structure of the hammer drill cannot be understood without disassembling it. The following main components are hidden in the plastic case:
- Electric motor;
- Safety clutch;
- "Drunk" bearing;
- Flying piston;
- Cartridge.
The principle of operation of the hammer drill consists in converting the rotation of the electric motor into the shock-rotational movement of the nozzles. The electric motor drives the rest of the hammer drill mechanism. The safety clutch ensures the safety of specialists during work. The drunken bearing drives the piston, creating an impact force, and the chuck secures the nozzles. Now let’s talk more about each of these nodes.
Electric motor
The main parts of the electric motor. stator and rotor.
The stator windings create a constant electromagnetic field inside which the rotor rotates. There are several windings on the rotor. The leads of the coils are connected to the armature contacts. At the same time, one of the windings is included in the electrical circuit. Power is supplied through graphite brushes to the armature contacts. By switching the windings, a slip field is created, due to which the rotor rotates.
The electric motor in the tool can be horizontal and vertical. The horizontal is usually used in light rock drills, while the medium and high power models are equipped with a vertical electric motor.
The operation of the electric part of the hammer drill is regulated by a trigger mechanism by pressing a button on the handle.
Safety clutch
To stop the rotation of the chuck if the working nozzle is jammed, a safety clutch is installed in the hammer drills. This is a necessary element: without its use, a powerful tool turns out of hand, the continuation of the independent rotation of the hammer drill easily leads to injuries to the worker. In rock drills, two main types of clutch devices are used: friction or cam.
- Under normal operating conditions of the tool, the friction clutch discs are tightly pressed against each other. this is how the rotational force is transferred to the rest of the mechanism. If rotation is hindered, the discs slide without overloading the drive.
- In the cam clutch, both halves of it have beveled projections that fit into the grooves of the counterpart. The half-couplings are connected with a spring of a certain stiffness. If the force on the impact mechanism exceeds the spring pressure, the tabs will protrude from the slots, disengaging the clutch. During this, a characteristic rattle is heard, for which the cam clutch is often called a ratchet.
What the puncher consists of
The controls are located on the body of the tool, as can be seen in the following photo:
The internal structure of the hammer drill cannot be understood without disassembling it. The following main components are hidden in the plastic case:
- Electric motor;
- Safety clutch;
- "Drunk" bearing;
- Flying piston;
- Cartridge.
The principle of operation of the hammer drill consists in converting the rotation of the electric motor into the shock-rotational movement of the nozzles. The electric motor drives the rest of the hammer drill mechanism. The safety clutch ensures the safety of specialists during work. The drunken bearing drives the piston, creating an impact force, and the chuck secures the nozzles. Now let’s talk more about each of these nodes.
Rotary hammer device and principle of operation
Cartridge
The hammer drill chuck is designed in such a way that the user has the opportunity to quickly change the accessory without making long interruptions in work. We are talking about two main types of cartridges:
- SDS-plus;
- SDS-max.
Tool shank for SDS-plus chuck is clamped with two locking balls.
SDS-max chucks accept tools with different shanks for more secure clamping.
How to Repair a Makita Rotary Hammer?
To determine the cause of the breakdown, you need to disassemble the cartridge. You need to disassemble as follows:
- First of all, the lever is dismantled.
- Next, the cartridge is disassembled. To do this, take a screwdriver and remove the rubber gasket. Then the retaining ring is removed.
- After that, all other elements are removed.
Chuck problems can be as follows:
- The gasket is worn out. If this happens, you need to clean the tool from dust and replace the dust cover.
- Cover deformation. In this case, the element is replaced.
- The retaining ring relaxed. The element should be slightly tightened if possible. If not, then the part must be replaced.
- If the ball is worn out, then you need to install a new part, lubricate it and fix it in the hole of the guide washer.
- If the ball guide is worn, then the level of wear should be determined. If it is small, then it is enough to lubricate the part. In case of heavy wear, the element must be replaced.
- The conical spring is the most durable element, but it can also wear out from time to time. The part must be positioned with the smaller vertex towards the gearbox.
The cartridge is assembled in the reverse order. Finally, you need to lubricate the end of the drill.
The main malfunction of rotary hammers
If you know the structure of a punch, you can easily replace a broken part. In most cases, the repair of this tool is reduced to replacing the elements that are out of order. These include:
- Switches;
- Anchor;
- Brushes;
- Gears;
- Starter;
- Bearings.
Professional device malfunctions can be complex. Only highly qualified specialists are capable of handling some of them. Such problems are often encountered: breakdown of the winding, rewinding of the armature and starter. These faults are caused by dust. Repair consists in cleaning and replacing elements. From time to time it is necessary to carry out preventive maintenance. it is recommended to clean the device once every 2 weeks. Special attention should be paid to the choice of lubricant; if such a mixture is not available, a diesel oil can be used.
Another cause of breakage is brush wear. Replacing them is very simple: you should disassemble the perforator according to the scheme described above, find worn brushes and install new ones in their place. You will need to determine exactly which ones are suitable. Brushes can be carbon, graphite or carbon-graphite. Graphite has a long service life, however, the hardness of the material can damage the collector. Coal tools have a short service life, but they have good contact with other elements of the rock drill. If the funds that can be allocated for the replacement of brushes are not very much, then it is recommended to use carbon-graphite brushes.
There may be problems with the mechanical parts of the device.
Safety clutch
To stop the rotation of the chuck if the working nozzle is jammed, a safety clutch is installed in the hammer drills. This is a necessary element: without its use, a powerful tool turns out of hand, the continuation of the independent rotation of the hammer drill easily leads to injuries to the worker. In rock drills, two main types of clutch devices are used: friction or cam.
- Under normal operating conditions of the tool, the friction clutch discs are tightly pressed against each other. this is how the rotational force is transferred to the rest of the mechanism. If rotation is hindered, the discs slide without overloading the drive.
- In the cam clutch, both halves of it have beveled projections that fit into the grooves of the counterpart. The half-couplings are connected with a spring of a certain stiffness. If the force on the impact mechanism exceeds the spring pressure, the tabs will protrude from the slots, disengaging the clutch. During this, a characteristic rattle is heard, for which the cam clutch is often called a ratchet.
About percussion mechanisms
In the design of the power tools under consideration, impact mechanisms of two types are used:
- Electromechanical
- Electro-pneumatic
Electro-pneumatic devices are very popular, and electromechanical ones are no longer used. They are based on a drunken bearing that drives a piston. The piston travels in a bushing where the compressed air is pressurized. This air acts on the impact firing pin, which moves from the piston to the heel of the installed nozzle in the hammer chuck.
How does a straight hammer drill work?
The principle of the hammer drill is based on the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy. The electric motor is driven by supplying current from a 220V household network. The rotor rotates in the engine, which drives the gearbox. The gearbox transmits the force to the chuck of the power tool, in which the corresponding accessory is fixed. This is a short description of how the rock drill works. When repairing or replacing parts of the power tool in question, it does not fit to understand the details of the principle of operation of the device:
- To begin with, you need to fix the working nozzle in the tool holder, which is quite simple. With one hand, you need to press the plastic sleeve of the chuck to the body, and then insert the drill into the device. Do not forget to lubricate the accessory shanks before installing them in the power tool chuck.
- The plug is respectively inserted into the socket, which is necessary for the operation of the electric motor
- When the start button is pressed, an electric current is supplied to the stator of the electric motor, due to which an electromagnetic field is created. The rotor is supplied with current through graphite brushes and a collector. When a current enters the rotor, it moves under the influence of the resulting magnetic field. Two magnetic fields with different poles repel each other, which we see when a collector electric motor is running
- The stator shaft is centered and supported by bearings that allow it to rotate. over, the rotation of the shaft reaches a speed of 27,000 rpm
- At the end of the rotor shaft there is a small helical gear, which meshes with the transmission mechanism of the scouring shaft. a gear of large diameter. Due to this, there is a decrease in rotation speed and an increase in torque. Usually all tools have a constant gear ratio and the speed is electronically controlled.
- The ram shaft is the shaft containing the gears and the drunken bearing. The gear wheel, connected to the shaft of the electric motor, drives the rotary hammer shaft
- A drunk bearing is attached to the ram shaft, as well as a small-diameter gear that meshes with a large-diameter gear located on the axis of the raster sleeve
- The shock option is realized due to the skewed rotation of the drunk bearing. The protrusion from the drunk bearing (perpendicular axis) is connected to the piston or elongated sleeve. This sleeve is located inside the flare sleeve, where it moves in a reciprocating or oscillatory manner.
- A sleeve with an impact striker moves inside the raster sleeve or barrel. In the sleeve, where the firing pin moves, there is an air space due to which the part is influenced. The piston builds up air pressure, thereby acting on the movable firing pin. Under the influence of compressed air pressure, the striker moves, acting with the striking part on the striking bolt or striker. The striker serves to transfer the resulting impact force from the striker to the heel of the installed nozzle in the hammer drill chuck. The striker travel is about 3-4 mm. On the striker there is a sealing gum, which develops over time, which manifests itself in the form of a decrease in the impact function (the impact force decreases). To restore the previous impact force of the instrument, it is necessary to replace the rubber band on the striker
- The gear wheel from the scouring shaft transmits the force to the gear, fixed on the raster sleeve and located perpendicular to the scouring shaft. The gear, which is attached to the raster sleeve and transfers the rotational force to the chuck, is designed to reduce the frequency of movement of the chuck
As a result, the hammer drill operates in the hammer drilling mode. In addition to the hammer drilling mode, pistol units are also capable of drilling without hammering or working in the hammer mode. To do this, the design of the power tool has a switch that turns off the rotation of a drunk bearing or gear on the shaft, depending on the mode being switched on. By the way, the drilling function is turned off due to jamming of the gear located on the raster sleeve.
The power tool can be used not only for processing concrete and other durable structures, but also for processing metal, wood, plastic and glass. Knowing how a straight puncher works, it will not be difficult to find the cause of its malfunction, as well as eliminate it. Often, if the parts of the perforator fail, they need to be replaced. over, depending on the scale of the breakdown, it may be necessary to replace either the entire mechanism. a gearbox, or individual parts. a drunk bearing, a striker, gears.
The hammer mechanism on the hammer drill works exclusively under load, therefore, at idle, when the installed nozzle is not pressed against the work surface, the tool will not create an impact. This is achieved due to the fact that the impact firing pin moves inside the raster sleeve, however, due to the absence of compression (pressure), this movement is idle. As soon as the nozzle is installed in the chuck and pressed against the treated surface, the channel overlaps in the area of the shank end location, due to which compression is created. In the presence of compression, the force of the working stroke of the striker increases, acting on the heel of the installed nozzle. This force is called impact force and is measured in Joules. In pistol perforators, the impact force reaches 2-3 Joules, and in professional barrel models up to 20 Joules.
The principle of operation of pistol-type DeWalt rock drills is described above. All pistol perforators of the brands Interskol, Energomash, Bosch, Stern, Makita, Hilti and others work on a similar principle.
The principle of operation of a pistol-type perforator with a photo description
The need to purchase a puncher always arises as soon as it is planned to carry out independent repairs in a house or apartment. After choosing the appropriate model of power tool, the owner needs to learn how to use the tool. To do this, you need to find out the principle of operation of the punch, as well as find out the features of its use.
About safety couplings
Such devices (safety clutches) are required on all perforators of household, semi-professional and professional type. They are used in order to stop the rotation of the chuck when the nozzle is jammed. If the clutch is defective, the following consequences may occur when seized:
- A jammed nozzle increases the current flowing in the rotor and stator windings, which contributes to the melting of the insulation and the failure of the electric motor
- Highly powerful hammer drill can rip out of your hands if the bit gets stuck, resulting in serious injury.
Safety couplings are of two types:
- The friction clutch is the most common modification of the protective mechanism, which is realized through the use of a gear mechanism. The toothed discs are tightly pressed against each other, transferring the rotational force. When the drill gets jammed, the discs slip, which eliminates the overload of the electric drive
- Cam or spring-cam couplings. consist of two halves with beveled projections that engage with the slots of the counterpart. These halves are called half couplings, which are connected by means of springs of the appropriate stiffness. As soon as a large force is generated that exceeds the spring pressure, the half-couplings are disengaged. When disengaging the half-couplings, a corresponding crackle is formed, as on screwdrivers. This is how the ratchet works on the power tool in question. Such couplings have one significant drawback. it is the rolling of the protrusions, therefore, with the time of operation of the tool, a crackle occurs even when the drills do not jam. The photo below shows the essence of the rolling problem, which can be eliminated even without replacing the gear with rolled teeth (for this it is necessary to eliminate the rolling places)
- Roller devices are another type of safety clutches. They are also installed in the structure of the transmission gear, and when the nozzle is jammed, the transmission gear, which drives the chuck, begins to turn. They are called roller due to the use of a roller-shaped locking key. Due to this key, installed in the groove of the bushing, the gear engages, as well as the transfer of rotational force. When the load increases (when the nozzle is jammed), under the action of the spring, the gear is displaced along the axis of the barrel, thereby engaging with the locking teeth (blockade) located on the perforator body (on the inside). Once the drill is free to move again, the spring force is reduced and the gear returns to its original position.
The photo below shows the details of the hammer drill, as well as the gearbox with the roller clutch installed. To find out which sleeve is installed on the hammer drill, you need to disassemble it. In addition, there are also magnetic clutches, but they are not used on small and medium power rock drills.
Perforator cartridges
Structurally, perforators use two main types of cartridges. SDS-plus and SDS-max. There are other types, but these two types of executive bodies are considered the most popular and effective. SDS-plus is used on household and semi-professional type machines, and SDS-max on professional rotary hammers.
In the material, it should be noted only that the attachments in such chucks are not fixed rigidly, as in collet chucks. The nozzle installed in the chuck has free play, which plays an important role in the impact mechanism. It is due to this stroke that shock effects are performed on the treated surface.
The attachments are fixed due to the slots, the number of which is two in SDS-plus cartridges, and three in SDS-max devices. These splines are guides and also allow the drills to rotate with the chuck. In addition to the splines, the design of the devices contains balls (in SDS-plus chucks) and rollers (SDS-max). They engage with grooves in the nozzle shank structure. It is due to the balls and rollers that the movable fixation of the nozzles is ensured.
So, having figured out the device of the power tool, it’s time to move on to the question of how the hammer drill works. The principle of its operation is simple, but it is impossible to deal with it without disassembling the power tool. To do this, you need to disassemble the tool and examine the component parts. In order not to have to disassemble the punch, we will find out how it works using the photo description.
Perforator straight what it is and what does it consist of
Structurally, the tool under consideration is of two types. pistol or straight and barrel. They differ not only externally, but also structurally. We will understand in detail what a pistol and barrel perforator is, how they work, as well as the features of their correct use.
Externally, the tool has a plastic case on which the controls are located. These bodies include (for direct and pistol-type perforators):
- Trigger for turning on the tool and adjusting the speed of rotation of the executive body. chuck
- Switch lock. allows you to prevent the tool from turning on independently, and also eliminates the need to hold the trigger, which is convenient when performing long work
- Reverse switch. allows you to switch the direction of rotation of the chuck in two directions
- Knob for switching the operating modes of the tool
- Chuck speed regulator. not available on all hammer drill models
- Additional handle for ease of work
- The executive body is a cartridge, inside which nozzles are fixed depending on the tasks
The inside of the power tool consists of the following elements:
- The electric motor is the “heart” of the tool, which powers the chuck.
- Gearbox. Rotational energy is transmitted to the gearbox, which allows speed control and also creates a shock effect. The gearbox consists of gears, as well as a special mechanism, due to which shock actions are created
- The safety clutch is an accessory part that prevents tool failure when the accessory gets stuck in the work surface. If the drill jams, the electric motor can burn out
- An anti-vibration system is a device that reduces vibration. Such a system is relevant, since during prolonged work with a puncher, not only fatigue occurs, but also tremors of the hands. In barrel rock drills, this system is also more advanced than pistol types.
These are the main internal mechanisms of the power tool, which you need to familiarize yourself with in order to understand the principle of the hammer drill. So, in order to find out how a hammer drill works, you need to understand the internal mechanisms.
What the puncher consists of
There are two types of perforators:
- Pistol or straight.
Both types differ not so much externally as in design, but, accordingly, have a different field of application.
Barrel puncher
The barrel type is distinguished by the quality of the above details, as well as their location. The design is radically different due to the location of the motor. This entails some changes.
Such a device is best used in professional activities. It has tremendous power, rotational speed and impact force. This technique is classified as heavy.
Scheme
The internal circuits of both types are similar:
- Electric motor. powers the device using the rest of the mechanism.
- Gear unit. responsible for rotation speed and impact force. Has a separate clear mechanism and takes over half of the entire punching activity.
- Safety clutch. prevents the failure of an electrical device if some part stops working.
- Anti-vibration system. minimizes vibrations for greater precision.
Pistol and straight rock drill
Let us consider in more detail the structure of the first type. It has a plastic housing on which the control panel is located:
- Power button and power regulator at the same time.
- Retainer. Prevents the device from turning on independently due to the owner’s negligence, and also fixes the device in the selected mode, which allows you not to hold the power button throughout the entire operation.
- Chuck rotation switch (changes direction).
- Switch for changing operating modes.
- Rotation speed switch.
- Second handle, allowing you to more securely hold the electrical device in your hands.
- The cartridge is an executive body, also important for changing nozzles.
Such a hammer drill is more suitable for domestic or semi-professional work, where the power that it has is enough. This type belongs to the category of lungs and is used more like a drill.
The device and principle of operation of the punch
Any power tool needs timely maintenance. Sometimes it is enough to simply lubricate it, but serious breakdowns occur that require elimination. This will help the instructions, which will describe the device and the principle of operation of the punch, but the information attached to the tool is not always enough, in which case additional sources will help.
- What the puncher consists of
- Pistol and straight rock drill
- Barrel puncher
- Scheme
- Principle of operation and modes
Principle of operation and modes
There are three main modes in the work of the punch:
- Rotating Impact. Enables you to drill through hard and thick surfaces effortlessly.
- Non-spinning kick. allows you to hit concrete surfaces.
- Rotation without impact. turns the hammer drill into a drill.
The principle of operation of the device is simple:
- A current flows through the electric motor, launching the rest of the mechanism.
- The stator shaft begins to rotate due to its location on the bearings. At its end there is a helical gear, which reduces speed and increases torque.
- Due to the rotation of the bearing, an impact option arises.
This causes all the parts inside the rock drill to move and interact with each other, transferring energy to the gear, which regulates the power and operation of the rock drill.
Punch wiring diagram
In general, the electrical circuit of the hammer drill may differ significantly for different models, and in its simplest version it is similar to the electrical circuit of an electric drill, which is described in detail in the article Drill device.
Impact mechanism
There are two main versions of the electro-pneumatic shock mechanism. Using an oscillating ("drunk") bearing or crank mechanism. The first option is used for light and, partially, medium perforators, the second. For medium to heavy.
The figure below shows a diagram of a light type perforator. Its impact mechanism consists of an oscillating bearing, piston, ram and striker.
When the rock drill is in operation, the rotation from the electric motor is transmitted to the inner bushing of the oscillating bearing. In this case, its outer sleeve, together with the perpendicular axis connected to the piston, makes oscillatory movements. Between the piston and the ram there is an air space, which, due to the alternately created increased pressure and vacuum, forces the ram to repeat the oscillatory movements of the piston, striking the striker. The latter, in turn, strikes the tool in the chuck. Thus, the energy of the electric motor is transformed into the impact energy of the tool.
The pneumatic percussion mechanism is equipped with a self-shutdown function when idling. At a time when the tool (drill, drill, crown) is not pressed against the work surface, the ram moves forward, opening a hole in the body for air inlet and outlet. As a result, compression and vacuum in the working air cavity are not created, the impact mechanism is turned off, and the hammer drill works without impacts. When the tool is pressed on the surface to be treated, the hole is closed with a ram, compression occurs in the air cavity, and the impact mechanism begins to function.
In medium and heavy rock drills with a vertical engine layout, the piston is driven by a crank mechanism. The increased amplitude of piston movement contributes to a higher impact power, which in heavy rock drills can reach 20 J. The impact mechanism operates in the same way as described above.
At the end of the article there is a demonstration of the work of the percussion mechanism.
The figure below shows the device of a domestically produced perforator Progress PE-40/1050, with a power of 1050 W with a vertical engine and a crank drive of the percussion mechanism. Rotation from the engine through the worm shaft is transmitted to the helical gear, on the shaft of which there is a crank that drives the piston.
Punch device
Engine location
The horizontal layout is used, as a rule, in light rock drills, vertical. Medium to heavy. However, there are exceptions. Heavy hammer drill Metabo KHE 96 with a weight of almost 12 kg has a horizontal motor.
The horizontal tool is more compact and convenient for working in tight spaces. However, this design is characterized by an increased shock load on the engine and somewhat worse conditions for its cooling.
The vertical arrangement provides better engine operating conditions (reduced shock vibration and efficient cooling), as well as a wider range of piston and striker movement due to the ability to use a crank mechanism with an increased piston stroke instead of a swing bearing.
Vertical rock drills can handle more work than the horizontal rock drills.
Anti-vibration system
At the end of the article there is a demonstration of the work of an active anti-vibration system.
In addition, the handle can also be responsible for damping vibration: from below it is attached to the body with a hinge, and from above through a spring mechanism. The passive anti-vibration system refers to the usual rubber pads on the case, which also protect against slipping of the hand. However, we must admit that the use of overlays is not too great.